0.前言
多传感器融合(Multi-sensor Fusion, MSF)是利用计算机技术,将来自多传感器或多源的信息和数据以一定的准则进行自动分析和综合,以完成所需的决策和估计而进行的信息处理过程。和人的感知相似,不同的传感器拥有其他传感器不可替代的作用,当各种传感器进行多层次,多空间的信息互补和优化组合处理,最终产生对观测环境的一致性解释。
具体来讲,多传感器数据融合处理:
(1)多个不同类型传感器(有源或无源)收集观测目标的数据;
(2)对传感器的输出数据(离散或连续的时间函数数据、输出矢量、成像数据或一个直接的属性说明)进行特征提取的变换,提取代表观测数据的特征矢量Yi;
(3)对特征矢量Yi进行模式识别处理(如聚类算法、自适应神经网络或其他能将特征矢量Yi变换成目标属性判决的统计模式识别法等),完成各传感器关于目标的说明;
(4)将各传感器关于目标的说明数据按同一目标进行分组,即关联;
(5)利用融合算法将目标的各传感器数据进行合成,得到该目标的一致性解释与描述。
1.多传感器融合分类
后端融合算法
后端融合算法又被称为松耦合算法,本质上是对融合后的多维综合数据进行感知,如下图所示,后端融合算法是松散的,在出结果之前,所有的传感器都是独立的,不存在传感器与传感器的约束。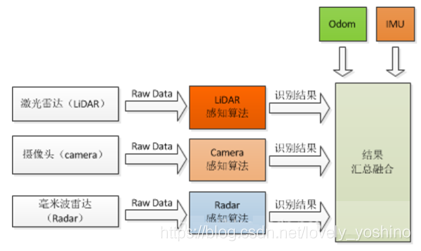
这种后端融合方法常见的融合策略是使用EKF或ESKF来实现(一般常见于LIO当中)。这样会导致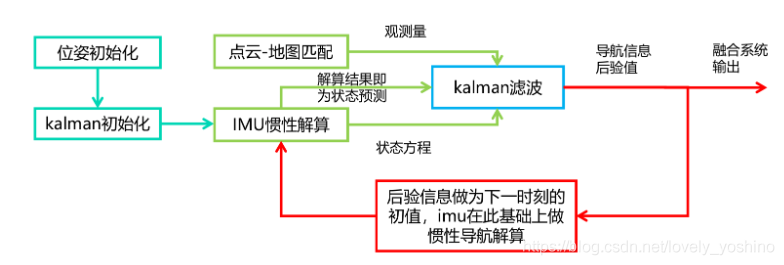
#include <aruco_ekf_slam/aruco_ekf_slam.h>
ArUcoEKFSLAM::ArUcoEKFSLAM (const cv::Mat& K, const cv::Mat& dist,
const double& kl, const double kr, const double& b,
const Eigen::Matrix4d& T_r_c,
const double& k, const double& k_r, const double k_phi,
const int& n_markers, const int& marker_size, const double& marker_length ):
K_(K), dist_(dist), kl_(kl), kr_(kr), b_(b), T_r_c_(T_r_c), k_(k), k_r_(k_r), k_phi_(k_phi),
n_markers_(n_markers), marker_size_(marker_size), marker_length_(marker_length)
{
is_init_ = false;
/* 初始时刻机器人位姿为0,绝对准确, 协方差为0 */
mu_.resize(3, 1);
mu_.setZero();
sigma_.resize(3, 3);
sigma_.setZero();
dictionary_ = cv::aruco::generateCustomDictionary(n_markers_, marker_size_);
}
void ArUcoEKFSLAM::addEncoder ( const double& enl, const double& enr )
{
if( is_init_ == false)
{
last_enl_ = enl;
last_enr_ = enr;
is_init_ = true;
return;
}
/***** 编码器数据预处理 *****/
/* 计算 Delta_l/r */
double delta_enl = enl - last_enl_;
double delta_enr = enr - last_enr_;
double delta_sl = kl_ * delta_enl;
double delta_sr = kr_ * delta_enr;
/* 计算 Delta theta and Delta s */
double delta_theta = (delta_sr - delta_sl) / b_;
double delta_s = 0.5 * (delta_sr + delta_sl);
/***** 更新均值 *****/
double tmp_th = mu_(2,0) + 0.5 * delta_theta;
double cos_tmp_th = cos( tmp_th );
double sin_tmp_th = sin(tmp_th);
mu_(0, 0) += delta_s * cos_tmp_th;
mu_(1, 0) += delta_s * sin_tmp_th;
mu_(2, 0) += delta_theta;
normAngle(mu_(2, 0)); //norm
/***** 更新协方差 *****/
/* 构造 G_xi */
Eigen::Matrix3d G_xi;
G_xi << 1.0, 0.0, -delta_s * sin_tmp_th,
0.0, 1.0, delta_s * cos_tmp_th,
0.0, 0.0, 1.0;
/* 构造 Gu' */
Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 2> Gup;
Gup << 0.5 * (cos_tmp_th - delta_s * sin_tmp_th / b_), 0.5 * (cos_tmp_th + delta_s * sin_tmp_th / b_),
0.5 * (sin_tmp_th + delta_s * cos_tmp_th /b_), 0.5 *(sin_tmp_th - delta_s * cos_tmp_th/b_),
1.0/b_, -1.0/b_;
int N = mu_.rows();
Eigen::MatrixXd F(N, 3); F.setZero();
F.block(0,0, 3, 3) = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity();
Eigen::MatrixXd Gt = Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(N, N);
Gt.block(0, 0, 3, 3) = G_xi;
/* 构造控制协方差 */
Eigen::Matrix2d sigma_u;
sigma_u << k_ * k_ * delta_sr * delta_sr, 0.0, 0.0, k_ * k_* delta_sl * delta_sl;
/* 更新协方差 */
sigma_ = Gt * sigma_ *Gt.transpose() + F * Gup * sigma_u * Gup.transpose() * F.transpose();
/***** 保存上一帧编码器数据 *****/
last_enl_ = enl;
last_enr_ = enr;
}
void ArUcoEKFSLAM::addImage ( const cv::Mat& img )
{
if( is_init_ == false)
return;
std::vector< Observation > obs;
getObservations(img, obs);
for( Observation ob: obs)
{
/* 计算观测方差 */
Eigen::Matrix2d Q;
Q << k_r_ * k_r_* fabs(ob.r_ * ob.r_), 0.0, 0.0, k_phi_ * k_phi_ * fabs(ob.phi_ * ob.phi_);
int i; // 第 i 个路标
if(checkLandmark(ob.aruco_id_, i))// 如果路标已经存在了
{
int N = mu_.rows();
Eigen::MatrixXd F(5, N);
F.setZero();
F.block(0,0,3,3) = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity();
F(3, 3 + 2*i) = 1;
F(4, 4 + 2*i) = 1;
double& mx = mu_(3 + 2*i, 0);
double& my = mu_(4 + 2*i, 0);
double& x = mu_(0,0);
double& y = mu_(1,0);
double& theta = mu_(2,0);
double delta_x = mx - x;
double delta_y = my -y;
double q = delta_x * delta_x + delta_y * delta_y;
double sqrt_q = sqrt(q);
Eigen::MatrixXd Hv(2, 5);
Hv << -sqrt_q * delta_x, -sqrt_q* delta_y, 0, sqrt_q*delta_x, sqrt_q*delta_y,
delta_y, -delta_x, -q, -delta_y, delta_x;
Hv = (1/q) * Hv;
Eigen::MatrixXd Ht = Hv * F;
Eigen::MatrixXd K = sigma_ * Ht.transpose()*( Ht * sigma_ * Ht.transpose() + Q ).inverse();
double phi_hat = atan2(delta_y, delta_x)- theta;
normAngle(phi_hat);
Eigen::Vector2d z_hat(
sqrt_q, phi_hat
);
Eigen::Vector2d z(ob.r_, ob.phi_);
mu_ = mu_ + K * (z - z_hat);
Eigen::MatrixXd I = Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(N, N);
sigma_ = ( I - K * Ht) * sigma_;
}else // 添加新路标
{
/* 均值 */
double angle = mu_(2,0) + ob.phi_; normAngle(angle);
double mx = ob.r_ * cos(angle) + mu_(0,0);
double my = ob.r_ * sin(angle) + mu_(1,0);
Eigen::Matrix3d sigma_xi = sigma_.block(0,0, 3, 3);
Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 3> Gp;
Gp << 1, 0, -ob.r_ * sin(angle),
0, 1, ob.r_ * cos(angle);
Eigen::Matrix2d Gz;
Gz << cos(angle), -ob.r_ * sin(angle),
sin(angle), ob.r_ * cos(angle);
// 新地图点的协方差
Eigen::Matrix2d sigma_m = Gp * sigma_xi * Gp.transpose() + Gz * Q * Gz.transpose();
// 新地图点相对于已有状态的协方差
Eigen::MatrixXd Gfx;
Gfx.resize ( 2, mu_.rows() );
Gfx.setZero();
Gfx.block ( 0,0, 2, 3 ) = Gp;
Eigen::MatrixXd sigma_mx;
sigma_mx.resize ( 2, mu_.rows() );
sigma_mx.setZero();
sigma_mx = Gfx * sigma_;
/**** 加入到地图中 ****/
/* 扩展均值 */
int N = mu_.rows();
Eigen::MatrixXd tmp_mu ( N + 2, 1 );
tmp_mu.setZero();
tmp_mu << mu_ , mx, my;
mu_.resize ( N+2, 1 );
mu_ = tmp_mu;
/* 扩展协方差 */
Eigen::MatrixXd tmp_sigma ( N+2, N+2 );
tmp_sigma.setZero();
tmp_sigma.block ( 0, 0, N, N ) = sigma_;
tmp_sigma.block ( N, N, 2, 2 ) = sigma_m;
tmp_sigma.block ( N, 0, 2, N ) = sigma_mx;
tmp_sigma.block ( 0, N, N, 2 ) = sigma_mx.transpose();
sigma_.resize ( N+2, N+2 );
sigma_ = tmp_sigma;
/***** 添加id *****/
aruco_ids_.push_back ( ob.aruco_id_ );
}// add new landmark
}// for all observation
}
int ArUcoEKFSLAM::getObservations ( const cv::Mat& img, std::vector< Observation >& obs )
{
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point2f>> marker_corners;
std::vector<int> IDs;
std::vector<cv::Vec3d> rvs, tvs;
cv::aruco::detectMarkers(img, dictionary_ , marker_corners, IDs);
cv::aruco::estimatePoseSingleMarkers(marker_corners, marker_length_, K_, dist_, rvs, tvs);
/* draw all marks */
marker_img_ = img.clone();
cv::aruco::drawDetectedMarkers(marker_img_, marker_corners, IDs);
for(size_t i=0; i<IDs.size(); i++)
cv::aruco::drawAxis(marker_img_, K_, dist_, rvs[i], tvs[i], 0.07);
/* 筛选距离较近的使用 */
const float DistTh = 3; //3 m
for ( size_t i = 0; i < IDs.size(); i ++ )
{
float dist = cv::norm<double>(tvs[i]); //计算距离
if( dist > DistTh)
continue;
/* 转化一下成Eigen T */
cv::Vec3d tvec = tvs[i];
cv::Vec3d rvec = rvs[i];
cv::Mat R;
cv::Rodrigues(rvec, R);
Eigen::Matrix4d T_c_m;
T_c_m <<
R.at<double>(0, 0), R.at<double>(0, 1), R.at<double>(0, 2), tvec[0],
R.at<double>(1, 0), R.at<double>(1, 1), R.at<double>(1, 2), tvec[1],
R.at<double>(2, 0), R.at<double>(2, 1), R.at<double>(2, 2), tvec[2],
0.,0.,0.,1.;
Eigen::Matrix4d T_r_m = T_r_c_ * T_c_m;
double& x= T_r_m(0, 3);
double& y = T_r_m(1, 3);
double r = sqrt(x*x + y*y);
double phi = atan2(y, x);
int aruco_id = IDs[i];
/* 加入到观测vector */
obs.push_back( Observation( aruco_id, r, phi));
}//for all detected markers
return obs.size();
}
visualization_msgs::MarkerArray ArUcoEKFSLAM::toRosMarkers(double scale)
{
visualization_msgs::MarkerArray markers;
int N = 0;
for(int i = 4; i < mu_.rows(); i+=2)
{
double& mx = mu_(i-1, 0);
double& my = mu_(i, 0);
/* 计算地图点的协方差椭圆角度以及轴长 */
Eigen::Matrix2d sigma_m = sigma_.block(i-1, i-1, 2, 2); //协方差
cv::Mat cvsigma_m = (cv::Mat_<double>(2,2) <<
sigma_m(0,0), sigma_m(0,1), sigma_m(1,0), sigma_m(1,1));
cv::Mat eigen_value, eigen_vector;
cv::eigen(cvsigma_m, eigen_value, eigen_vector);
double angle = atan2( eigen_vector.at<double>(0, 1), eigen_vector.at<double>(0, 0));
double x_len = 2 * sqrt(eigen_value.at<double>(0,0) * 5.991) ;
double y_len = 2 * sqrt( eigen_value.at<double>(1,0)* 5.991);
/* 构造marker */
visualization_msgs::Marker marker;
marker.header.frame_id = "world";
marker.header.stamp = ros::Time();
marker.ns = "ekf_slam";
marker.id = i;
marker.type = visualization_msgs::Marker::SPHERE;
marker.action = visualization_msgs::Marker::ADD;
marker.pose.position.x = mx;
marker.pose.position.y = my;
marker.pose.position.z = 0;
marker.pose.orientation = tf::createQuaternionMsgFromYaw(angle);
marker.scale.x = scale * x_len;
marker.scale.y = scale * y_len;
marker.scale.z = 0.1 * scale * (x_len + y_len);
marker.color.a = 0.8; // Don't forget to set the alpha!
marker.color.r = 0.0;
marker.color.g = 1.0;
marker.color.b = 0.0;
markers.markers.push_back(marker);
}// for all mpts
return markers;
}
geometry_msgs::PoseWithCovarianceStamped ArUcoEKFSLAM::toRosPose()
{
/* 转换带协方差的机器人位姿 */
geometry_msgs::PoseWithCovarianceStamped rpose;
rpose.header.frame_id = "world";
rpose.pose.pose.position.x = mu_(0, 0);
rpose.pose.pose.position.y = mu_(1, 0);
rpose.pose.pose.orientation = tf::createQuaternionMsgFromYaw(mu_(2, 0));
rpose.pose.covariance.at(0) = sigma_(0,0);
rpose.pose.covariance.at(1) = sigma_(0,1);
rpose.pose.covariance.at(6) = sigma_(1,0);
rpose.pose.covariance.at(7) = sigma_(1,1);
rpose.pose.covariance.at(5) = sigma_(0,2);
rpose.pose.covariance.at(30) = sigma_(2,0);
rpose.pose.covariance.at(35) = sigma_(2,2);
return rpose;
}
void ArUcoEKFSLAM::normAngle ( double& angle )
{
const static double PI = 3.1415926;
static double Two_PI = 2.0 * PI;
if( angle >= PI)
angle -= Two_PI;
if( angle < -PI)
angle += Two_PI;
}
// 暴力搜素
bool ArUcoEKFSLAM::checkLandmark ( int aruco_id, int& landmark_idx )
{
for(size_t i = 0; i < aruco_ids_.size(); i ++)
{
if(aruco_id == aruco_ids_.at(i))
{
landmark_idx = i;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
前端融合算法
本质上就是每个传感器作为一部分融合成一个单一的传感器,从整体上来考虑信息,这样做的好处是在前端时候即可融合数据,让这些数据具有关联性,例如当VSLAM在平地行走时,缺少Z轴方向上的激励,这是时通过里程计等传感器的前端融合可以较好地避免系统的衰减。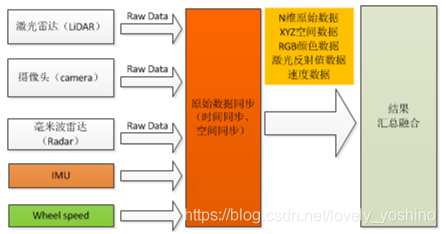
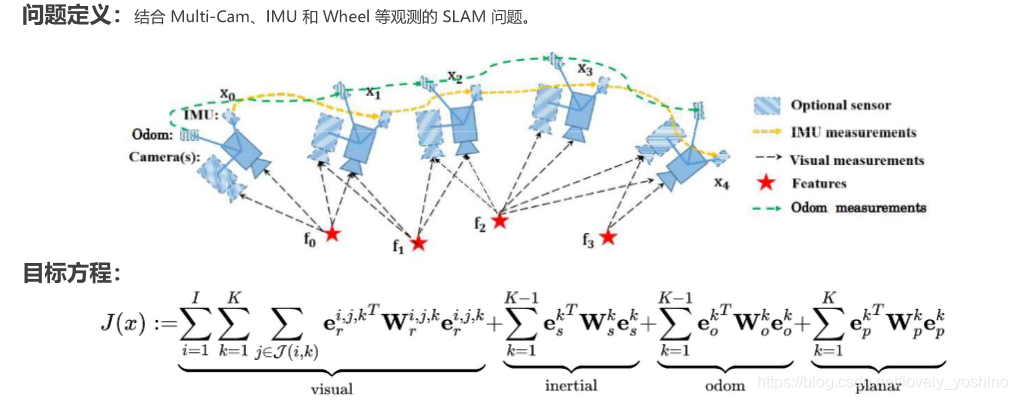
这一类现在是松耦合中常用的策略,基于Ceres函数库对环境进行优化(这一类松耦合方法一般都是基于VIO的)
#include "factor/Factors.h"
#include "optimization/multisensorOpt.h"
using namespace std;
MultisensorOptimization::MultisensorOptimization()
{
initGPS = false;
newGPS = false;
WGPS_T_WVIO = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity();
threadOpt = std::thread(&MultisensorOptimization::optimize, this);
windowLength = 50;
lastLocalP = Eigen::Vector3d::Zero();
}
MultisensorOptimization::~MultisensorOptimization()
{
threadOpt.detach();
}
void MultisensorOptimization::GPS2XYZ(double latitude, double longitude, double altitude, double *xyz)
{
if(!initGPS)
{
geoConverter.Reset(latitude, longitude, altitude);
initGPS = true;
}
geoConverter.Forward(latitude, longitude, altitude, xyz[0], xyz[1], xyz[2]);
}
void MultisensorOptimization::inputOdom(double t, Eigen::Vector3d odomP, Eigen::Quaterniond odomQ)
{
mPoseMap.lock();
vector<double> localPose{odomP.x(), odomP.y(), odomP.z(),
odomQ.w(), odomQ.x(), odomQ.y(), odomQ.z()};
// 位移差1厘米,才运动
if ((odomP - lastLocalP).norm() > 0.01)
{
localPoseMap[t] = localPose;
while (localPoseMap.size() > windowLength)
{
localPoseMap.erase(std::begin(localPoseMap));
}
Eigen::Quaterniond globalQ;
globalQ = WGPS_T_WVIO.block<3, 3>(0, 0) * odomQ;
Eigen::Vector3d globalP = WGPS_T_WVIO.block<3, 3>(0, 0) * odomP + WGPS_T_WVIO.block<3, 1>(0, 3);
vector<double> globalPose{globalP.x(), globalP.y(), globalP.z(),
globalQ.w(), globalQ.x(), globalQ.y(), globalQ.z()};
globalPoseMap[t] = globalPose;
while (globalPoseMap.size() > windowLength)
{
globalPoseMap.erase(std::begin(globalPoseMap));
}
lastLocalP = odomP;
}
mPoseMap.unlock();
}
void MultisensorOptimization::getGlobalOdom(Eigen::Vector3d &odomP, Eigen::Quaterniond &odomQ)
{
odomP = lastP;
odomQ = lastQ;
}
void MultisensorOptimization::inputGPS(double t, double latitude, double longitude, double altitude, double latCov, double lonCov, double altCov)
{
double xyz[3];
GPS2XYZ(latitude, longitude, altitude, xyz);
std::vector<double> tmp{xyz[0], xyz[1], xyz[2], latCov, lonCov, altCov};
// printf("new gps: t: %f x: %f y: %f z:%f \n", t, tmp[0], tmp[1], tmp[2]);
GPSPositionMap[t] = tmp;
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped poseStamped;
poseStamped.header.stamp = ros::Time(t);
poseStamped.header.frame_id = "world";
poseStamped.pose.position.x = tmp[0];
poseStamped.pose.position.y = tmp[1];
poseStamped.pose.position.z = tmp[2];
poseStamped.pose.orientation.w = 1;
poseStamped.pose.orientation.x = 0;
poseStamped.pose.orientation.y = 0;
poseStamped.pose.orientation.z = 0;
gpsPath.header = poseStamped.header;
gpsPath.poses.push_back(poseStamped);
newGPS = true;
}
void MultisensorOptimization::optimize()
{
while (true)
{
if (newGPS)
{
newGPS = false;
// printf("Multisensor optimization\n");
ceres::Problem problem;
ceres::Solver::Options options;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::SPARSE_NORMAL_CHOLESKY;
//options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true;
//options.max_solver_time_in_seconds = SOLVER_TIME * 3;
options.max_num_iterations = 5;
// options.max_solver_time_in_seconds = 0.15;
ceres::Solver::Summary summary;
ceres::LossFunction *lossFunction;
lossFunction = new ceres::HuberLoss(1.0);
ceres::LocalParameterization* local_parameterization = new ceres::QuaternionParameterization();
//add param
mPoseMap.lock();
int length = localPoseMap.size();
// w^t_i w^q_i
double t_array[length][3];
double q_array[length][4];
map<double, vector<double>>::iterator iter;
iter = globalPoseMap.begin();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++, iter++)
{
t_array[i][0] = iter->second[0];
t_array[i][1] = iter->second[1];
t_array[i][2] = iter->second[2];
q_array[i][0] = iter->second[3];
q_array[i][1] = iter->second[4];
q_array[i][2] = iter->second[5];
q_array[i][3] = iter->second[6];
problem.AddParameterBlock(q_array[i], 4, local_parameterization);
problem.AddParameterBlock(t_array[i], 3);
}
std::map<double, std::vector<double>>::iterator iterVIO, iterVIONext, iterGPS;
int i = 0;
for (iterVIO = localPoseMap.begin(); iterVIO != localPoseMap.end(); iterVIO++, i++)
{
//vio factor
iterVIONext = iterVIO;
iterVIONext++;
if (iterVIONext != localPoseMap.end())
{
Eigen::Matrix4d wTi = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity();
Eigen::Matrix4d wTj = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity();
wTi.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = Eigen::Quaterniond(iterVIO->second[3], iterVIO->second[4],
iterVIO->second[5], iterVIO->second[6]).toRotationMatrix();
wTi.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = Eigen::Vector3d(iterVIO->second[0], iterVIO->second[1], iterVIO->second[2]);
wTj.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = Eigen::Quaterniond(iterVIONext->second[3], iterVIONext->second[4],
iterVIONext->second[5], iterVIONext->second[6]).toRotationMatrix();
wTj.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = Eigen::Vector3d(iterVIONext->second[0], iterVIONext->second[1], iterVIONext->second[2]);
Eigen::Matrix4d iTj = wTi.inverse() * wTj;
Eigen::Quaterniond iQj;
iQj = iTj.block<3, 3>(0, 0);
Eigen::Vector3d iPj = iTj.block<3, 1>(0, 3);
ceres::CostFunction* vio_function = RelativeRTError::Create(iPj.x(), iPj.y(), iPj.z(),
iQj.w(), iQj.x(), iQj.y(), iQj.z(),
0.1, 0.01);
problem.AddResidualBlock(vio_function, NULL, q_array[i], t_array[i], q_array[i+1], t_array[i+1]);
/*
double **para = new double *[4];
para[0] = q_array[i];
para[1] = t_array[i];
para[3] = q_array[i+1];
para[4] = t_array[i+1];
double *tmp_r = new double[6];
double **jaco = new double *[4];
jaco[0] = new double[6 * 4];
jaco[1] = new double[6 * 3];
jaco[2] = new double[6 * 4];
jaco[3] = new double[6 * 3];
vioFunction->Evaluate(para, tmp_r, jaco);
std::cout << Eigen::Map<Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1>>(tmp_r).transpose() << std::endl
<< std::endl;
std::cout << Eigen::Map<Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 4, Eigen::RowMajor>>(jaco[0]) << std::endl
<< std::endl;
std::cout << Eigen::Map<Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 3, Eigen::RowMajor>>(jaco[1]) << std::endl
<< std::endl;
std::cout << Eigen::Map<Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 4, Eigen::RowMajor>>(jaco[2]) << std::endl
<< std::endl;
std::cout << Eigen::Map<Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 3, Eigen::RowMajor>>(jaco[3]) << std::endl
<< std::endl;
*/
}
// gps factor
double t = iterVIO->first;
iterGPS = GPSPositionMap.find(t);
if (iterGPS != GPSPositionMap.end())
{
ceres::CostFunction* gpsFunction = TError::Create(iterGPS->second[0], iterGPS->second[1], iterGPS->second[2],
iterGPS->second[3], iterGPS->second[4], iterGPS->second[5]);
problem.AddResidualBlock(gpsFunction, lossFunction, t_array[i]);
/*
double **para = new double *[1];
para[0] = t_array[i];
double *tmp_r = new double[3];
double **jaco = new double *[1];
jaco[0] = new double[3 * 3];
gpsFunction->Evaluate(para, tmp_r, jaco);
std::cout << Eigen::Map<Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 1>>(tmp_r).transpose() << std::endl
<< std::endl;
std::cout << Eigen::Map<Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 3, Eigen::RowMajor>>(jaco[0]) << std::endl
<< std::endl;
*/
}
}
// solve problem
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
// std::cout << summary.BriefReport() << std::endl;
// update global pose
iter = globalPoseMap.begin();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++, iter++)
{
vector<double> globalPose{t_array[i][0], t_array[i][1], t_array[i][2],
q_array[i][0], q_array[i][1], q_array[i][2], q_array[i][3]};
iter->second = globalPose;
if(i == length - 1)
{
Eigen::Matrix4d WVIO_T_body = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity();
Eigen::Matrix4d WGPS_T_body = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity();
double t = iter->first;
WVIO_T_body.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = Eigen::Quaterniond(localPoseMap[t][3], localPoseMap[t][4],
localPoseMap[t][5], localPoseMap[t][6]).toRotationMatrix();
WVIO_T_body.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = Eigen::Vector3d(localPoseMap[t][0], localPoseMap[t][1], localPoseMap[t][2]);
WGPS_T_body.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = Eigen::Quaterniond(globalPose[3], globalPose[4],
globalPose[5], globalPose[6]).toRotationMatrix();
WGPS_T_body.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = Eigen::Vector3d(globalPose[0], globalPose[1], globalPose[2]);
WGPS_T_WVIO = WGPS_T_body * WVIO_T_body.inverse();
}
}
updateGlobalPath();
mPoseMap.unlock();
}
// std::chrono::milliseconds dura(1000);
// std::this_thread::sleep_for(dura);
}
return;
}
void MultisensorOptimization::updateGlobalPath()
{
// global_path.poses.clear();
if (globalPath.poses.size() > windowLength - 1)
{
int i = windowLength - 1;
while (i > 0)
{
globalPath.poses.pop_back();
i--;
}
}
else
{
globalPath.poses.clear();
}
map<double, vector<double>>::iterator iter;
for (iter = globalPoseMap.begin(); iter != globalPoseMap.end(); iter++)
{
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped poseStamped;
poseStamped.header.stamp = ros::Time(iter->first);
poseStamped.header.frame_id = "world";
poseStamped.pose.position.x = iter->second[0];
poseStamped.pose.position.y = iter->second[1];
poseStamped.pose.position.z = iter->second[2];
poseStamped.pose.orientation.w = iter->second[3];
poseStamped.pose.orientation.x = iter->second[4];
poseStamped.pose.orientation.y = iter->second[5];
poseStamped.pose.orientation.z = iter->second[6];
globalPath.header = poseStamped.header;
globalPath.poses.push_back(poseStamped);
}
// 使用优化后的最新位姿作为global odometry
iter--;
lastP.x() = iter->second[0];
lastP.y() = iter->second[1];
lastP.z() = iter->second[2];
lastQ.w() = iter->second[3];
lastQ.x() = iter->second[4];
lastQ.y() = iter->second[5];
lastQ.z() = iter->second[6];
}
2.多传感器融合方式分类
松耦合
松耦合将多传感器(以视觉传感器和 IMU为例)作为两个单独的模块,两个模块均可以计算得到位姿信息,然后再进行融合。(意思基本就是图像通过特征点估算出位姿,然后和imu结合统一优化位姿【当中不涉及原始数据】)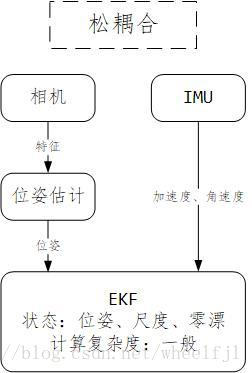
松耦合情况下滤波与优化的对比图。从图中可以看出,优化的优势并不是很明显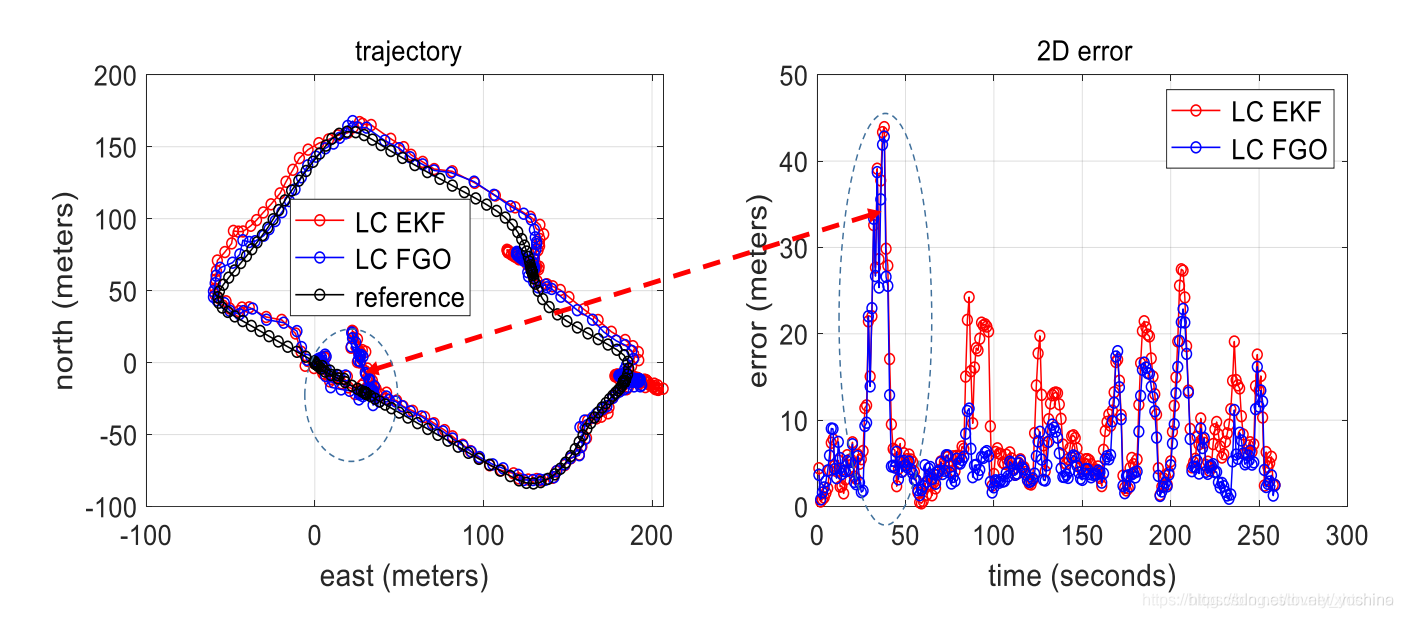
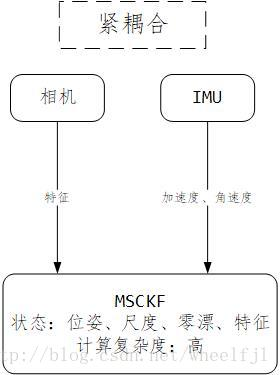
紧耦合
紧耦合则是指将多传感器(以视觉和 IMU为例)得到的中间数据通过一个优化滤波器进行处理,紧耦合需要把图像特征加入到特征向量中,最终得到位姿信息的过程。由于这个原因,系统状态向量最终的维度也会非常高,同时计算量也很大。(意思基本就是图像拿出特征点,然后通过残差项来优化传感器信息,【当中涉及原始数据】)
//i时刻相机坐标系下的map point的逆深度
double inv_dep_i = parameters[3][0];
//i时刻相机坐标系下的map point坐标
Eigen::Vector3d pts_camera_i = pts_i / inv_dep_i;
//i时刻IMU坐标系下的map point坐标
Eigen::Vector3d pts_imu_i = qic * pts_camera_i + tic;
//世界坐标系下的map point坐标
Eigen::Vector3d pts_w = Qi * pts_imu_i + Pi;
//在j时刻imu坐标系下的map point坐标
Eigen::Vector3d pts_imu_j = Qj.inverse() * (pts_w - Pj);
//在j时刻相机坐标系下的map point坐标
Eigen::Vector3d pts_camera_j = qic.inverse() * (pts_imu_j - tic);
Eigen::Map<Eigen::Vector2d> residual(residuals);
#ifdef UNIT_SPHERE_ERROR
residual = tangent_base * (pts_camera_j.normalized() - pts_j.normalized());
#else
double dep_j = pts_camera_j.z();
residual = (pts_camera_j / dep_j).head<2>() - pts_j.head<2>();
#endif
紧耦合情况下滤波与优化的对比图 ,从图中可以看出,优化的优势较为明显。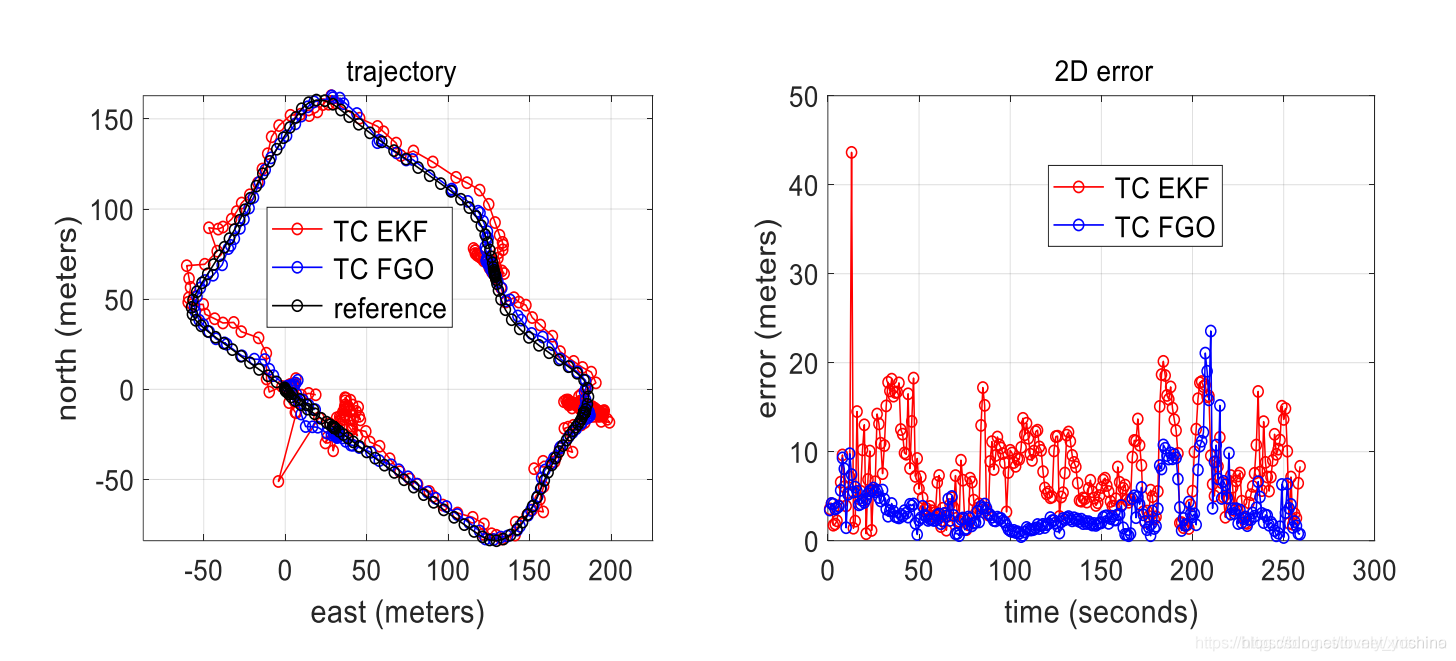
同样如果我们拥有GNSS的原始数据,也可以通过以下代码实现紧耦合
for (uint32_t j = 0; j < gnss_meas_buf[0].size(); ++j)
{
const uint32_t sys = satsys(gnss_meas_buf[0][j]->sat, NULL);
const uint32_t sys_idx = gnss_comm::sys2idx.at(sys);
const double obs_local_ts = time2sec(gnss_meas_buf[0][j]->time) - diff_t_gnss_local;
const double lower_ts = Headers[0].stamp.toSec();
const double upper_ts = Headers[1].stamp.toSec();
const double ts_ratio = (upper_ts-obs_local_ts) / (upper_ts-lower_ts);
GnssPsrDoppFactor *gnss_factor = new GnssPsrDoppFactor(gnss_meas_buf[0][j],
gnss_ephem_buf[0][j], latest_gnss_iono_params, ts_ratio);
ResidualBlockInfo *psr_dopp_residual_block_info = new ResidualBlockInfo(gnss_factor, NULL,
vector<double *>{para_Pose[0], para_SpeedBias[0], para_Pose[1],
para_SpeedBias[1],para_rcv_dt+sys_idx, para_rcv_ddt,
para_yaw_enu_local, para_anc_ecef},
vector<int>{0, 1, 4, 5});
marginalization_info->addResidualBlockInfo(psr_dopp_residual_block_info);
}
const double gnss_dt = Headers[1].stamp.toSec() - Headers[0].stamp.toSec();
for (size_t k = 0; k < 4; ++k)
{
DtDdtFactor *dt_ddt_factor = new DtDdtFactor(gnss_dt);
ResidualBlockInfo *dt_ddt_residual_block_info = new ResidualBlockInfo(dt_ddt_factor, NULL,
vector<double *>{para_rcv_dt+k, para_rcv_dt+4+k, para_rcv_ddt, para_rcv_ddt+1},
vector<int>{0, 2});
marginalization_info->addResidualBlockInfo(dt_ddt_residual_block_info);
}
// margin rcv_ddt smooth factor
DdtSmoothFactor *ddt_smooth_factor = new DdtSmoothFactor(GNSS_DDT_WEIGHT);
ResidualBlockInfo *ddt_smooth_residual_block_info = new ResidualBlockInfo(ddt_smooth_factor, NULL,
vector<double *>{para_rcv_ddt, para_rcv_ddt+1}, vector<int>{0});
marginalization_info->addResidualBlockInfo(ddt_smooth_residual_block_info);
3. 参考链接
https://blog.csdn.net/xhtchina/article/details/115560339
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/66724528
https://github.com/HKUST-Aerial-Robotics/GVINS






评论(0)
您还未登录,请登录后发表或查看评论