REVIEW: 贪婪最佳优先搜索算法Greedy Best-First Search
在上一篇blog中,主要是阐述了贪婪最佳优先启发式搜索算法,并通过一个简单的路径搜索的例子对其进行了应用。可以发现,GBFS启发式算法存在以下弊端:
1️⃣GBFS由于其评价机制的问题,产生的路径不是最优的;
2️⃣不完备性;
3️⃣在最坏的情况下,时间复杂度和空间复杂度都是 ,其中b是节点分支因子数目,m是搜索空间的最大深度。
在这篇blog中,主要是引入一种改进启发式搜索算法——A*,相对于GBFS,该算法的评价函数有两部分组成:
其中,h(n)仍为启发函数heuristic function,主要计算从节点n到目标节点之间所形成路径的最小代价值( 可以为曼哈顿距离,也可以为欧式距离... );g(n)表示从起始节点到节点n(之前花销)的开销代价。
为了进一步说明A*算法,我们通过 的path planning问题来进一步学习。
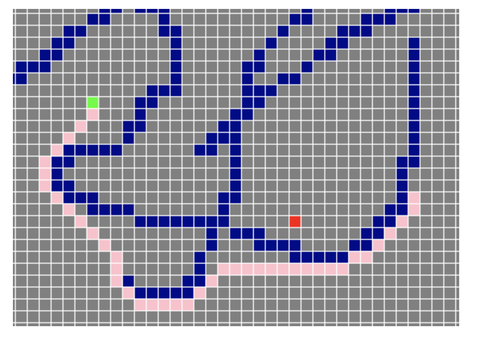
小车的grid planning
- 任务需求:寻找target并避障
- 算法:A*
- Heuristic:2D欧拉距离
- 图注:绿色——搜索路径,蓝色——目标点,红色——实际路径
- 网格尺寸:2.0/m
- 起始位置:可随机
- 目标位置:可随机
Step1: 搭建环境,我们采用grid环境,并设立垂直墙壁障碍物
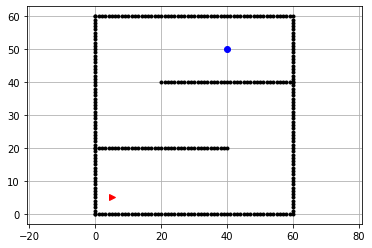
实现代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
%matplotlib inline
# global variable
show_animation = True
# 环境设置
def env():
# 初始与目标位置
sx = 5.0#/m
sy = 5.0 #/m
gx = 40 #/m
gy = 50 #/m
grid_size = 2.0 #/m 网格size
robot_radius = 1.0 #机器人范围
# 外墙
ox,oy = [],[]
for i in range(0,60):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(0)
for i in range(0,60):
ox.append(60)
oy.append(i)
for i in range(0,61):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(60)
for i in range(0,61):
ox.append(0)
oy.append(i)
# 内墙
for i in range(0,41):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(20)
for i in range(20,61):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(40)
plt.plot(ox,oy,".k")
plt.plot(sx,sy,">r")
plt.plot(gx,gy,"ob")
plt.grid(True)
plt.axis("equal")STEP2:搭建主题算法部分
首先要明确A*进行最优路径搜索的算法流程:
在这之前,我们review以下A*算法的评价函数:
其中:g(h)是从start到达指定grid的移动的cost;h(n)是从current的grid到达goal的估算cost,这里我们采用的是”欧式距离“作为计算标准。
1-建立一个open set
2-建立一个closed set
3- 重复下面过程:
3.1 --遍历open set,查找f(n)最小的node,把它作为当前需要被处理的node;
3.2 --把这个node移动到closed set
3.3 --对当前方格的相邻的方格,但是忽略已经放在closed set或者无法到达(碰到obstacle)的方格,若该方格不在open set中,则加入到open set中;若该方格已经在open_set中,检测由当前方格到达这个方格是否更好,用g(n)作为参考,更小的g值代表更好的路径,若是这样,把当前方格设置为新加入方格的parent,previous_index = current_index,并重新计算它的g(n)和f(n)值。
3.4 -- 若终点加入了open set中,stop.. 或者查找终点失败,并且open_list空,此时没有路径
4 - 保存路径,每个方格从goal开始,沿着parent node移动到start,即为该路径
具体代码如下:
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# author: IrvingHe
# email: irvinghe1518@gmail.com
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import math
# %matplotlib inline
# global variable
show_animation = True
class AStarPlannar:
def __init__(self, ox, oy, reso, rr):
"""
初始化
input:
ox --- 障碍物的x的坐标列表
oy --- 障碍物的y的坐标列表
reso --- grid的分辨率(grid solution)/m
rr --- 机器人半径/m
"""
self.reso = reso
self.rr = rr
self.calc_obstacle_map(ox, oy) # 计算地图(标出障碍物位置)
self.motion = self.get_motion_model()
class Node:
"""
节点属性定义
"""
def __init__(self, x, y, cost, pind):
self.x = x # x 索引
self.y = y # y 索引
self.cost = cost
self.pind = pind
def __str__(self):
"""返回节点信息,以字符串形式"""
return str(self.x) + "," + str(self.y) + "," + str(self.cost) + "," + str(self.pind)
def calc_obstacle_map(self, ox, oy):
"""
计算obstacle map
"""
self.minx = round(min(ox)) # 最小的x坐标
self.miny = round(min(oy)) # 最小的y坐标
self.maxx = round(max(ox)) # 最大的x坐标
self.maxy = round(max(oy)) # 最大的y坐标
print("minx:", self.minx)
print("miny:", self.miny)
print("maxx:", self.maxx)
print("maxy:", self.maxy)
self.xwidth = round((self.maxx - self.minx) / self.reso) # x方向有多少个网格
self.ywidth = round((self.maxy - self.miny) / self.reso) # y方向有多少个网格
print("xwidth:", self.xwidth)
print("ywidth:", self.ywidth)
# 生成obstacle map
self.obmap = [[False for i in range(self.ywidth)]
for i in range(self.xwidth)] # 初始化,xwidth x ywidth,全部为False
for ix in range(self.xwidth):
x = self.calc_grid_position(ix, self.minx) # 各个range的横坐标
for iy in range(self.ywidth):
y = self.calc_grid_position(iy, self.miny) # 各个range的纵坐标
for iox, ioy in zip(ox, oy):
d = math.hypot(iox - x, ioy - y)
if d <= self.rr:
self.obmap[ix][iy] = True # 标出有障碍物的位置 用于碰撞检测用
break
def calc_grid_position(self, index, minp):
"""
计算网格坐标
index: 网格索引号
minp:min x
"""
pos = index * self.reso + minp
return pos
def calc_grid_index(self, node):
"""
由节点计算index
"""
return (node.y - self.miny) * self.xwidth + (node.x - self.minx)
@staticmethod
def get_motion_model():
"""小车运动模型"""
# dx,dy,cost
motion = [[1, 0, 1], # 前
[0, 1, 1], # 上
[-1, 0, 1], # 后
[0, -1, 1], # 下
[-1, -1, math.sqrt(2)], # 左下
[-1, 1, math.sqrt(2)], # 左上
[1, -1, math.sqrt(2)], # 右下,
[1, 1, math.sqrt(2)]] # 右上
return motion
@staticmethod
def calc_heuristic(n1, n2):
"""
计算两节点之间的欧拉距离
"""
w = 1.0
d = w * math.hypot(n1.x - n2.x, n1.y - n2.y)
return d
def calc_xyindex(self, position, min_pos):
# 通过xy计算索引
return round((position - min_pos) / self.reso)
def verify_node(self, node):
"""检验节点是否超限或者发生碰撞"""
px = self.calc_grid_position(node.x, self.minx)
py = self.calc_grid_position(node.y, self.miny)
if px < self.minx:
return False
elif py < self.miny:
return False
elif px >= self.maxx:
return False
elif py >= self.maxy:
return False
# 碰撞检测
if self.obmap[node.x][node.y]: # 有True
return False
return True # safe
def calc_final_path(self, ngoal, closedset):
"""产生final路径"""
rx, ry = [self.calc_grid_position(ngoal.x, self.minx)], [self.calc_grid_position(ngoal.y, self.miny)]
pind = ngoal.pind
while pind != -1:
n = closedset[pind]
rx.append(self.calc_grid_position(n.x, self.minx))
ry.append(self.calc_grid_position(n.y, self.miny))
pind = n.pind
return rx, ry
def planning(self, sx, sy, gx, gy):
"""
A*路径规划算法
input:
sx:开始位置x坐标/m
sy:开始位置y坐标/m
gx:目标x位置/m
gy:目标y位置/m
output:
rx:最后路径的x位置列表
ry:最后路径的y位置列表
"""
# 初始node信息: x,y,cost,pind
nstart = self.Node(self.calc_xyindex(sx, self.minx),
self.calc_xyindex(sy, self.miny), 0.0, -1)
# 目标点node信息
ngoal = self.Node(self.calc_xyindex(gx, self.minx),
self.calc_xyindex(gy, self.miny), 0.0, -1)
open_set = dict()
closed_set = dict() # 空字典
open_set[self.calc_grid_index(nstart)] = nstart
while 1:
if len(open_set) == 0:
print("Open Set is Empty...")
break
# 两种知识取最小值得方案
c_id = min(open_set, key=lambda o: open_set[o].cost + self.calc_heuristic(ngoal, open_set[o]))
current = open_set[c_id] # 当前
# show_graph
if show_animation:
plt.plot(self.calc_grid_position(current.x, self.minx), # 计算x坐标
self.calc_grid_position(current.y, self.miny), # 坐标
"xc")
# -----按"esc"按键中断仿真程序-----
plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect('key_release_event',
lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
if len(closed_set.keys()) % 10 == 0:
plt.pause(0.001)
if current.x == ngoal.x and current.y == ngoal.y:
# 终点检测
print("Find goal")
ngoal.pind = current.pind
ngoal.cost = current.cost
break
# 从开放集中删除现在的item
del open_set[c_id]
# 将其添加到闭集中
closed_set[c_id] = current
# 基于运动模型搜索网格
for i, _ in enumerate(self.motion):
node = self.Node(current.x + self.motion[i][0], # x扩展
current.y + self.motion[i][1], # y扩展,
current.cost + self.motion[i][2], # cost扩展
c_id) # previous index换成当前index
n_id = self.calc_grid_index(node)
# 若Node不安全,舍弃
if not self.verify_node(node):
continue
if n_id in closed_set:
continue
if n_id not in open_set:
open_set[n_id] = node # 发现一个新节点
else:
if open_set[n_id].cost > node.cost:
# 到目前为止,该路径是最优的,记录下来
open_set[n_id] = node
rx, ry = self.calc_final_path(ngoal, closed_set)
return rx, ry
def main():
# 初始与目标位置
sx = 5.0#/m
sy = 5.0 #/m
gx = 40 #/m
gy = 50 #/m
grid_size = 2.0 #/m 网格size
robot_radius = 1.0 #机器人范围
# 外墙
ox,oy = [],[]
for i in range(0,60):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(0)
for i in range(0,60):
ox.append(60)
oy.append(i)
for i in range(0,61):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(60)
for i in range(0,61):
ox.append(0)
oy.append(i)
# 内墙
for i in range(0,41):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(20)
for i in range(20,61):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(40)
if show_animation:
plt.plot(ox,oy,".k")
plt.plot(sx,sy,">r")
plt.plot(gx,gy,"ob")
plt.grid(True)
plt.axis("equal")
a_star = AStarPlannar(ox,oy,grid_size,robot_radius)
rx,ry = a_star.planning(sx,sy,gx,gy)
if show_animation:
plt.plot(rx,ry,"--r")
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
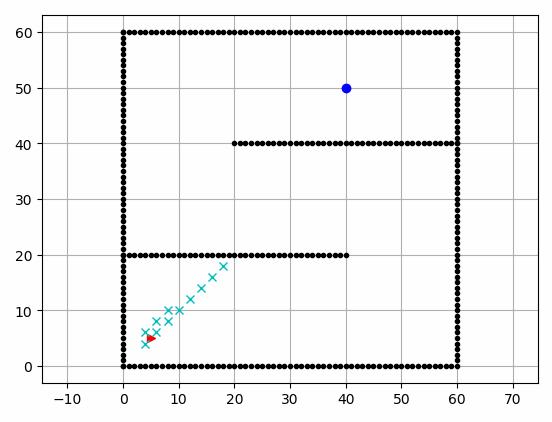
main()最终效果如下:







评论(0)
您还未登录,请登录后发表或查看评论