有关SORT的论文早先就已经拜读过了,一直想写这篇文章的源码解析,终于有时间来写了。
论文解读请参考:SIMPLE ONLINE AND REALTIME TRACKING (SORT)论文阅读笔记
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.00763
github地址:https://github.com/abewley/sort
以下用到的图片转自HaoBBNuanMM, 目的是为了更好的分析源码流程。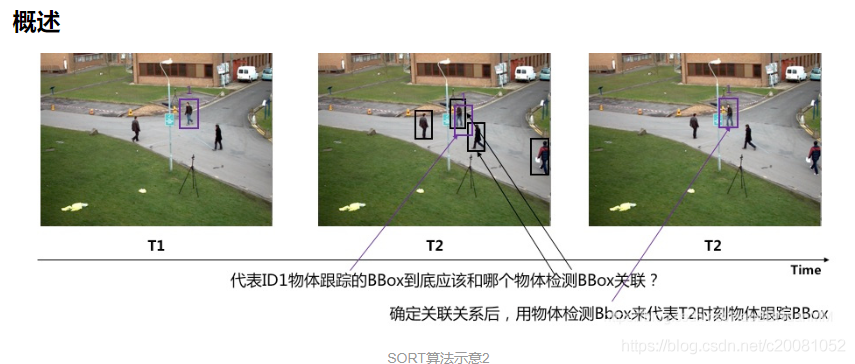




OK,接下来是源码分析,下载下来的项目代码中有如下内容:
主要就sort代码进行解析~
sort.py
"""
SORT: A Simple, Online and Realtime Tracker
Copyright (C) 2016 Alex Bewley alex@dynamicdetection.com
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
"""
from __future__ import print_function
from numba import jit #是python的一个JIT库,通过装饰器来实现运行时的加速
import os.path
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches #用于绘制常见图像(如矩形,椭圆,圆形,多边形)
from skimage import io
from sklearn.utils.linear_assignment_ import linear_assignment
import glob
import time
import argparse
from filterpy.kalman import KalmanFilter #filterpy包含了一些常用滤波器的库
@jit #用了jit装饰器,可加速for循环的计算
def iou(bb_test,bb_gt):
"""
Computes IOU between two bboxes in the form [x1,y1,x2,y2]
"""
xx1 = np.maximum(bb_test[0], bb_gt[0])
yy1 = np.maximum(bb_test[1], bb_gt[1])
xx2 = np.minimum(bb_test[2], bb_gt[2])
yy2 = np.minimum(bb_test[3], bb_gt[3])
w = np.maximum(0., xx2 - xx1)
h = np.maximum(0., yy2 - yy1)
wh = w * h
o = wh / ((bb_test[2]-bb_test[0])*(bb_test[3]-bb_test[1]) #IOU=(bb_test和bb_gt框相交部分面积)/(bb_test框面积+bb_gt框面积 - 两者相交面积)
+ (bb_gt[2]-bb_gt[0])*(bb_gt[3]-bb_gt[1]) - wh)
return(o)
def convert_bbox_to_z(bbox): #将bbox由[x1,y1,x2,y2]形式转为 [框中心点x,框中心点y,框面积s,宽高比例r]^T
"""
Takes a bounding box in the form [x1,y1,x2,y2] and returns z in the form
[x,y,s,r] where x,y is the centre of the box and s is the scale/area and r is
the aspect ratio
"""
w = bbox[2]-bbox[0]
h = bbox[3]-bbox[1]
x = bbox[0]+w/2.
y = bbox[1]+h/2.
s = w*h #scale is just area
r = w/float(h)
return np.array([x,y,s,r]).reshape((4,1)) #将数组转为4行一列形式,即[x,y,s,r]^T
def convert_x_to_bbox(x,score=None): #将[x,y,s,r]形式的bbox,转为[x1,y1,x2,y2]形式
"""
Takes a bounding box in the centre form [x,y,s,r] and returns it in the form
[x1,y1,x2,y2] where x1,y1 is the top left and x2,y2 is the bottom right
"""
w = np.sqrt(x[2]*x[3]) #w=sqrt(w*h * w/h)
h = x[2]/w #h=w*h/w
if(score==None): #如果检测框不带置信度
return np.array([x[0]-w/2.,x[1]-h/2.,x[0]+w/2.,x[1]+h/2.]).reshape((1,4)) #返回[x1,y1,x2,y2]
else: #如果加测框带置信度
return np.array([x[0]-w/2.,x[1]-h/2.,x[0]+w/2.,x[1]+h/2.,score]).reshape((1,5)) #返回[x1,y1,x2,y2,score]
class KalmanBoxTracker(object):
"""
This class represents the internel state of individual tracked objects observed as bbox.
"""
count = 0
def __init__(self,bbox):
"""
Initialises a tracker using initial bounding box. 使用初始边界框初始化跟踪器
"""
#define constant velocity model #定义匀速模型
self.kf = KalmanFilter(dim_x=7, dim_z=4) #状态变量是7维, 观测值是4维的,按照需要的维度构建目标
self.kf.F = np.array([[1,0,0,0,1,0,0],[0,1,0,0,0,1,0],[0,0,1,0,0,0,1],[0,0,0,1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,1]])
self.kf.H = np.array([[1,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,1,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,1,0,0,0]])
self.kf.R[2:,2:] *= 10.
self.kf.P[4:,4:] *= 1000. #give high uncertainty to the unobservable initial velocities 对未观测到的初始速度给出高的不确定性
self.kf.P *= 10. # 默认定义的协方差矩阵是np.eye(dim_x),将P中的数值与10, 1000相乘,赋值不确定性
self.kf.Q[-1,-1] *= 0.01
self.kf.Q[4:,4:] *= 0.01
self.kf.x[:4] = convert_bbox_to_z(bbox) #将bbox转为 [x,y,s,r]^T形式,赋给状态变量X的前4位
self.time_since_update = 0
self.id = KalmanBoxTracker.count
KalmanBoxTracker.count += 1
self.history = []
self.hits = 0
self.hit_streak = 0
self.age = 0
def update(self,bbox):
"""
Updates the state vector with observed bbox.
"""
self.time_since_update = 0
self.history = []
self.hits += 1
self.hit_streak += 1
self.kf.update(convert_bbox_to_z(bbox))
def predict(self):
"""
Advances the state vector and returns the predicted bounding box estimate.
"""
if((self.kf.x[6]+self.kf.x[2])<=0):
self.kf.x[6] *= 0.0
self.kf.predict()
self.age += 1
if(self.time_since_update>0):
self.hit_streak = 0
self.time_since_update += 1
self.history.append(convert_x_to_bbox(self.kf.x))
return self.history[-1]
def get_state(self):
"""
Returns the current bounding box estimate.
"""
return convert_x_to_bbox(self.kf.x)
def associate_detections_to_trackers(detections,trackers,iou_threshold = 0.3): #用于将检测与跟踪进行关联
"""
Assigns detections to tracked object (both represented as bounding boxes)
Returns 3 lists of matches, unmatched_detections and unmatched_trackers
"""
if(len(trackers)==0): #如果跟踪器为空
return np.empty((0,2),dtype=int), np.arange(len(detections)), np.empty((0,5),dtype=int)
iou_matrix = np.zeros((len(detections),len(trackers)),dtype=np.float32) # 检测器与跟踪器IOU矩阵
for d,det in enumerate(detections):
for t,trk in enumerate(trackers):
iou_matrix[d,t] = iou(det,trk) #计算检测器与跟踪器的IOU并赋值给IOU矩阵对应位置
matched_indices = linear_assignment(-iou_matrix) # 参考:https://blog.csdn.net/herr_kun/article/details/86509591 加上负号是因为linear_assignment求的是最小代价组合,而我们需要的是IOU最大的组合方式,所以取负号
unmatched_detections = [] #未匹配上的检测器
for d,det in enumerate(detections):
if(d not in matched_indices[:,0]): #如果检测器中第d个检测结果不在匹配结果索引中,则d未匹配上
unmatched_detections.append(d)
unmatched_trackers = [] #未匹配上的跟踪器
for t,trk in enumerate(trackers):
if(t not in matched_indices[:,1]): #如果跟踪器中第t个跟踪结果不在匹配结果索引中,则t未匹配上
unmatched_trackers.append(t)
#filter out matched with low IOU 过滤掉那些IOU较小的匹配对
matches = [] #存放过滤后的匹配结果
for m in matched_indices: #遍历粗匹配结果
if(iou_matrix[m[0],m[1]]<iou_threshold): #m[0]是检测器ID, m[1]是跟踪器ID,如它们的IOU小于阈值则将它们视为未匹配成功
unmatched_detections.append(m[0])
unmatched_trackers.append(m[1])
else:
matches.append(m.reshape(1,2)) #将过滤后的匹配对维度变形成1x2形式
if(len(matches)==0): #如果过滤后匹配结果为空,那么返回空的匹配结果
matches = np.empty((0,2),dtype=int)
else: #如果过滤后匹配结果非空,则按0轴方向继续添加匹配对
matches = np.concatenate(matches,axis=0)
return matches, np.array(unmatched_detections), np.array(unmatched_trackers) #其中跟踪器数组是5列的(最后一列是ID)
class Sort(object):
def __init__(self,max_age=1,min_hits=3):
"""
Sets key parameters for SORT
"""
self.max_age = max_age
self.min_hits = min_hits
self.trackers = []
self.frame_count = 0
def update(self,dets): #输入的是检测结果[x1,y1,x2,y2,score]形式
"""
Params:
dets - a numpy array of detections in the format [[x1,y1,x2,y2,score],[x1,y1,x2,y2,score],...]
Requires: this method must be called once for each frame even with empty detections. #每一帧都得调用一次,即便检测结果为空
Returns the a similar array, where the last column is the object ID. #返回相似的数组,最后一列是目标ID
NOTE: The number of objects returned may differ from the number of detections provided. #返回的目标数量可能与提供的检测数量不同
"""
self.frame_count += 1 #帧计数
#get predicted locations from existing trackers.
trks = np.zeros((len(self.trackers),5)) # 根据当前所有卡尔曼跟踪器的个数创建二维零矩阵,维度为:卡尔曼跟踪器ID个数x 5 (这5列内容为bbox与ID)
to_del = [] #存放待删除
ret = [] #存放最后返回的结果
for t,trk in enumerate(trks): #循环遍历卡尔曼跟踪器列表
pos = self.trackers[t].predict()[0] #用卡尔曼跟踪器t 预测 对应物体在当前帧中的bbox
trk[:] = [pos[0], pos[1], pos[2], pos[3], 0]
if(np.any(np.isnan(pos))): #如果预测的bbox为空,那么将第t个卡尔曼跟踪器删除
to_del.append(t)
trks = np.ma.compress_rows(np.ma.masked_invalid(trks)) #将预测为空的卡尔曼跟踪器所在行删除,最后trks中存放的是上一帧中被跟踪的所有物体在当前帧中预测的非空bbox
for t in reversed(to_del): #对to_del数组进行倒序遍历
self.trackers.pop(t) #从跟踪器中删除 to_del中的上一帧跟踪器ID
matched, unmatched_dets, unmatched_trks = associate_detections_to_trackers(dets,trks) #对传入的检测结果 与 上一帧跟踪物体在当前帧中预测的结果做关联,返回匹配的目标矩阵matched, 新增目标的矩阵unmatched_dets, 离开画面的目标矩阵unmatched_trks
#update matched trackers with assigned detections
for t,trk in enumerate(self.trackers): # 对卡尔曼跟踪器做遍历
if(t not in unmatched_trks): #如果上一帧中的t还在当前帧画面中(即不在当前预测的离开画面的矩阵unmatched_trks中)
d = matched[np.where(matched[:,1]==t)[0],0] #说明卡尔曼跟踪器t是关联成功的,在matched矩阵中找到与其关联的检测器d
trk.update(dets[d,:][0]) #用关联的检测结果d来更新卡尔曼跟踪器(即用后验来更新先验)
#create and initialise new trackers for unmatched detections #对于新增的未匹配的检测结果,创建并初始化跟踪器
for i in unmatched_dets: #新增目标
trk = KalmanBoxTracker(dets[i,:]) #将新增的未匹配的检测结果dets[i,:]传入KalmanBoxTracker
self.trackers.append(trk) #将新创建和初始化的跟踪器trk 传入trackers
i = len(self.trackers)
for trk in reversed(self.trackers): #对新的卡尔曼跟踪器集进行倒序遍历
d = trk.get_state()[0] #获取trk跟踪器的状态 [x1,y1,x2,y2]
if((trk.time_since_update < 1) and (trk.hit_streak >= self.min_hits or self.frame_count <= self.min_hits)):
ret.append(np.concatenate((d,[trk.id+1])).reshape(1,-1)) # +1 as MOT benchmark requires positive
i -= 1
#remove dead tracklet
if(trk.time_since_update > self.max_age):
self.trackers.pop(i)
if(len(ret)>0):
return np.concatenate(ret)
return np.empty((0,5))
def parse_args():
"""Parse input arguments."""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='SORT demo')
parser.add_argument('--display', dest='display', help='Display online tracker output (slow) [False]',action='store_true')
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
if __name__ == '__main__':
# all train
sequences = ['PETS09-S2L1','TUD-Campus','TUD-Stadtmitte','ETH-Bahnhof','ETH-Sunnyday','ETH-Pedcross2','KITTI-13','KITTI-17','ADL-Rundle-6','ADL-Rundle-8','Venice-2']
args = parse_args()
display = args.display
phase = 'train'
total_time = 0.0
total_frames = 0
colours = np.random.rand(32,3) #used only for display
if(display):
if not os.path.exists('mot_benchmark'):
print('\n\tERROR: mot_benchmark link not found!\n\n Create a symbolic link to the MOT benchmark\n (https://motchallenge.net/data/2D_MOT_2015/#download). E.g.:\n\n $ ln -s /path/to/MOT2015_challenge/2DMOT2015 mot_benchmark\n\n')
exit()
plt.ion() #用于动态绘制显示图像
fig = plt.figure()
if not os.path.exists('output'):
os.makedirs('output')
for seq in sequences:
mot_tracker = Sort() #create instance of the SORT tracker 创建Sort 跟踪实例
seq_dets = np.loadtxt('data/%s/det.txt'%(seq),delimiter=',') #load detections #加载检测结果
with open('output/%s.txt'%(seq),'w') as out_file:
print("Processing %s."%(seq))
for frame in range(int(seq_dets[:,0].max())): #确定视频序列总帧数,并进行for循环
frame += 1 #detection and frame numbers begin at 1 #由于视频序列帧数是从1开始的,因此加1
dets = seq_dets[seq_dets[:,0]==frame,2:7] #提取检测结果中的[x1,y1,w,h,score]到dets
dets[:,2:4] += dets[:,0:2] #convert to [x1,y1,w,h] to [x1,y1,x2,y2] 将dets中的第2,3列的数加上第0,1列的数后赋值给2,3列;
total_frames += 1 #总帧数累计
if(display): #如果要求显示结果
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111, aspect='equal')
fn = 'mot_benchmark/%s/%s/img1/%06d.jpg'%(phase,seq,frame) #原图像路径名
im =io.imread(fn) #加载图像
ax1.imshow(im) #显示图像
plt.title(seq+' Tracked Targets')
start_time = time.time()
trackers = mot_tracker.update(dets) #sort跟踪器更新
cycle_time = time.time() - start_time #sort跟踪器耗时
total_time += cycle_time #sort跟踪器总共耗费时间
for d in trackers:
print('%d,%d,%.2f,%.2f,%.2f,%.2f,1,-1,-1,-1'%(frame,d[4],d[0],d[1],d[2]-d[0],d[3]-d[1]),file=out_file) #打印: frame,ID,x1,y1,x2,y2,1,-1,-1,-1
if(display): #如果显示,将目标检测框画上
d = d.astype(np.int32)
ax1.add_patch(patches.Rectangle((d[0],d[1]),d[2]-d[0],d[3]-d[1],fill=False,lw=3,ec=colours[d[4]%32,:]))
ax1.set_adjustable('box-forced')
if(display):
fig.canvas.flush_events()
plt.draw()
ax1.cla()
print("Total Tracking took: %.3f for %d frames or %.1f FPS"%(total_time,total_frames,total_frames/total_time))
if(display):
print("Note: to get real runtime results run without the option: --display")
源码中是对视频图像序列的检测结果进行离线操作,用的检测器第fasrer-rcnn,检测的结果存放在data/视频名/det.txt中。
参考(这篇文章写得真的不错):【算法分析】SORT/Deep SORT 物体跟踪算法解析






评论(0)
您还未登录,请登录后发表或查看评论