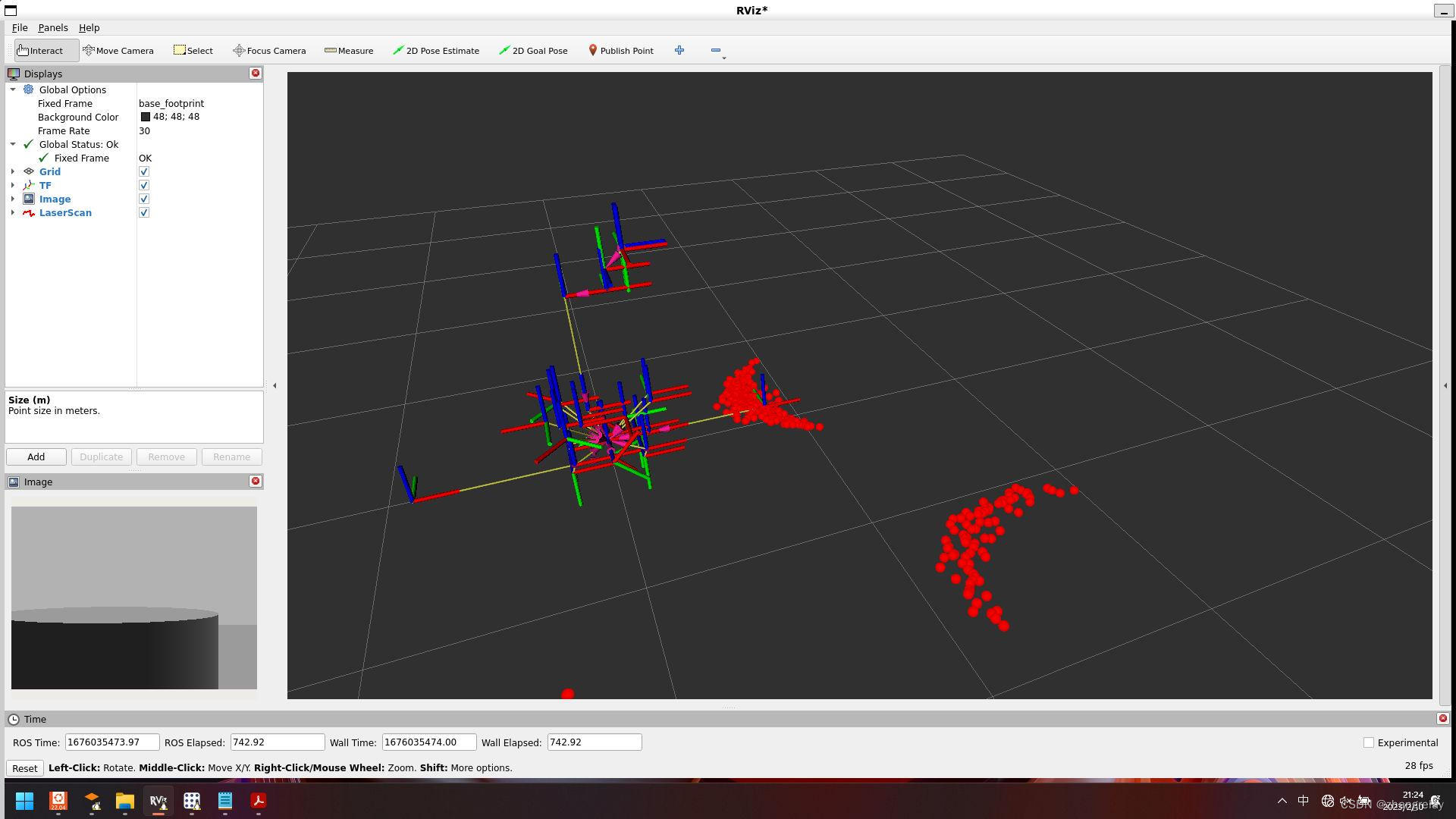
下图所示,机器人和障碍物直接距离:
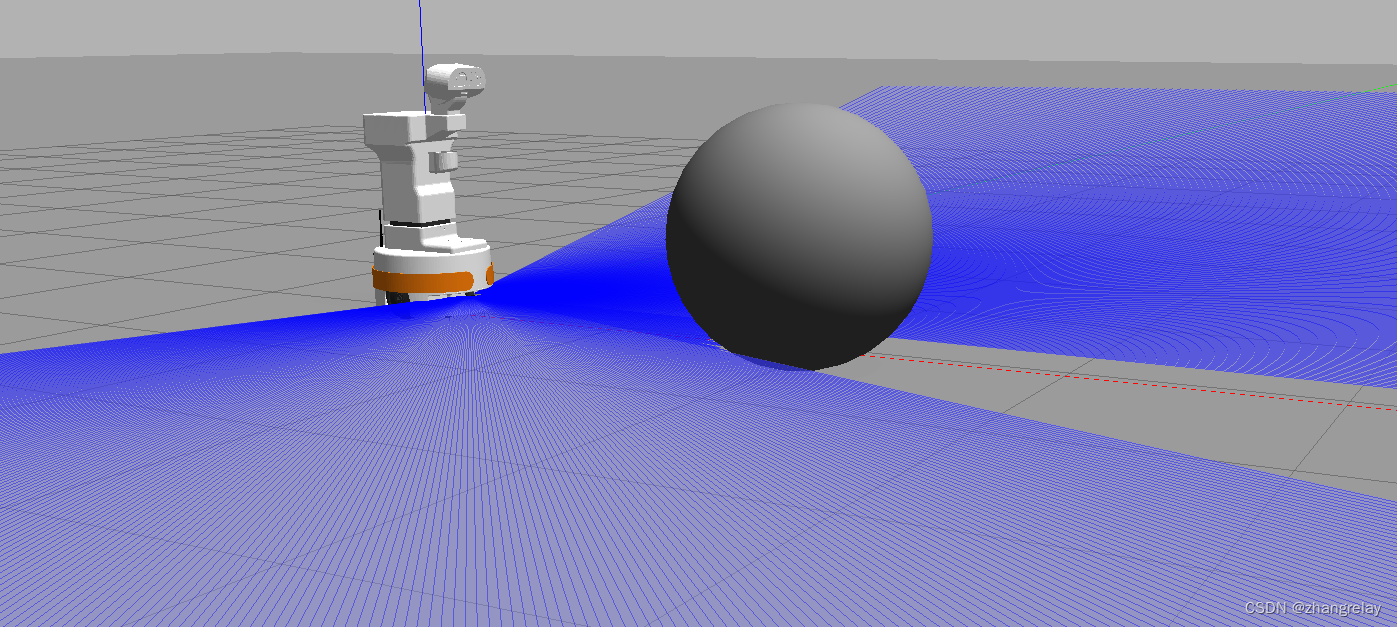
可以看到如果是单线雷达,这种测距和传感器安装的位置密切相关。
chatgpt:
ROS2机器人的COMPUTATION GRAPH概念是指,通过构建一个图形结构,将机器人的计算任务分解成一系列的可执行步骤。其特点是具有易于理解、可扩展性强的特性,可以有效地提高机器人的计算性能。它的应用可以帮助机器人实现自主操作、自主导航等功能。
ROS2机器人激光测距系统的计算图是一种用于检测和定位物体的技术。它可以利用激光雷达发射的脉冲,经过反射后再次接收,从而测量物体到激光雷达的距离。它通常由一个传感器,一个处理器,一个控制器和一个软件组成,它们可以在ROS2机器人系统中实现自动控制和导航。
书中给出的图示:

使用rqt工具获取,与此一致:
测得距离等,成功会有一组数据显示。
例如,turtlebot
例如,tiago
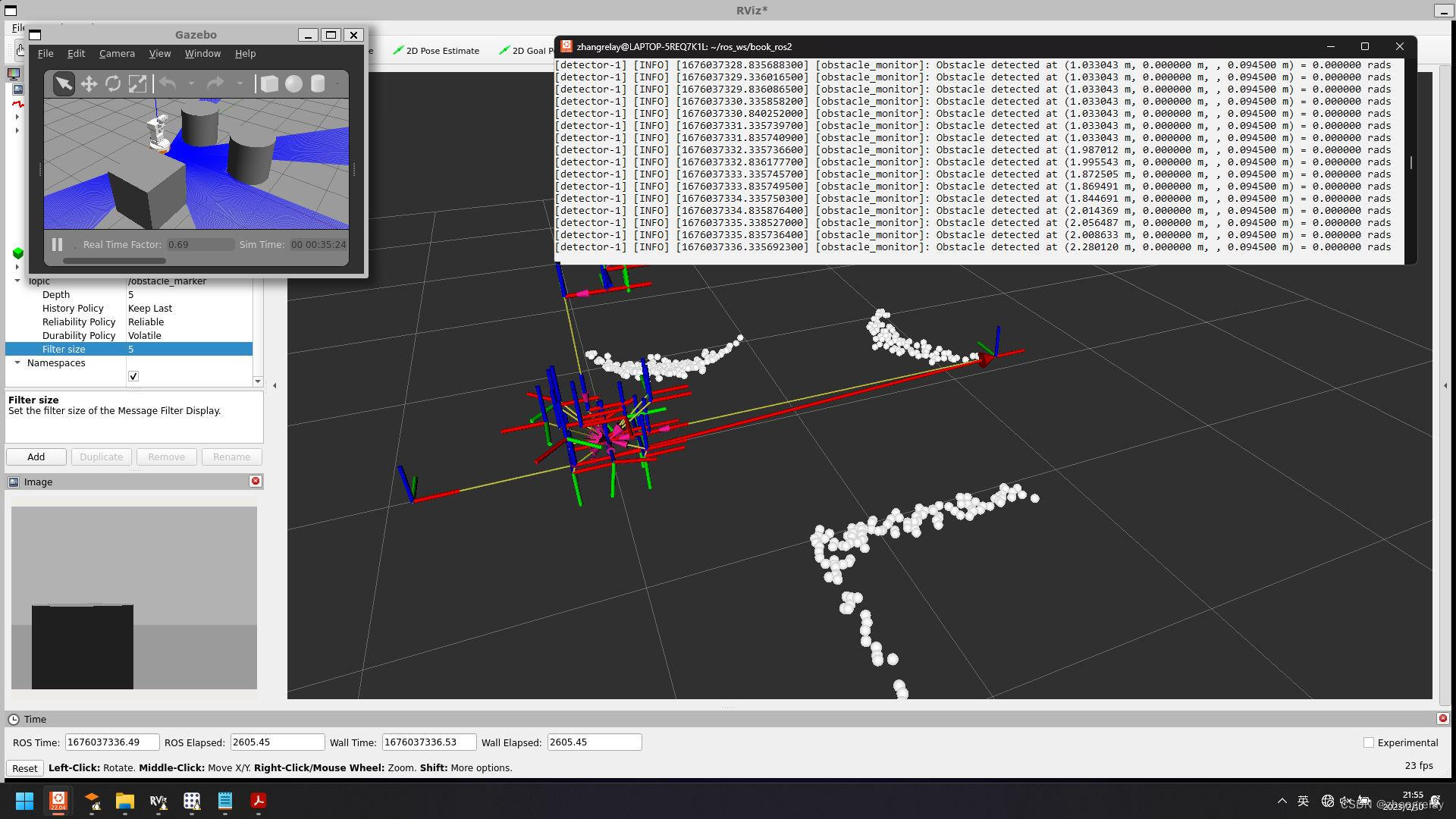
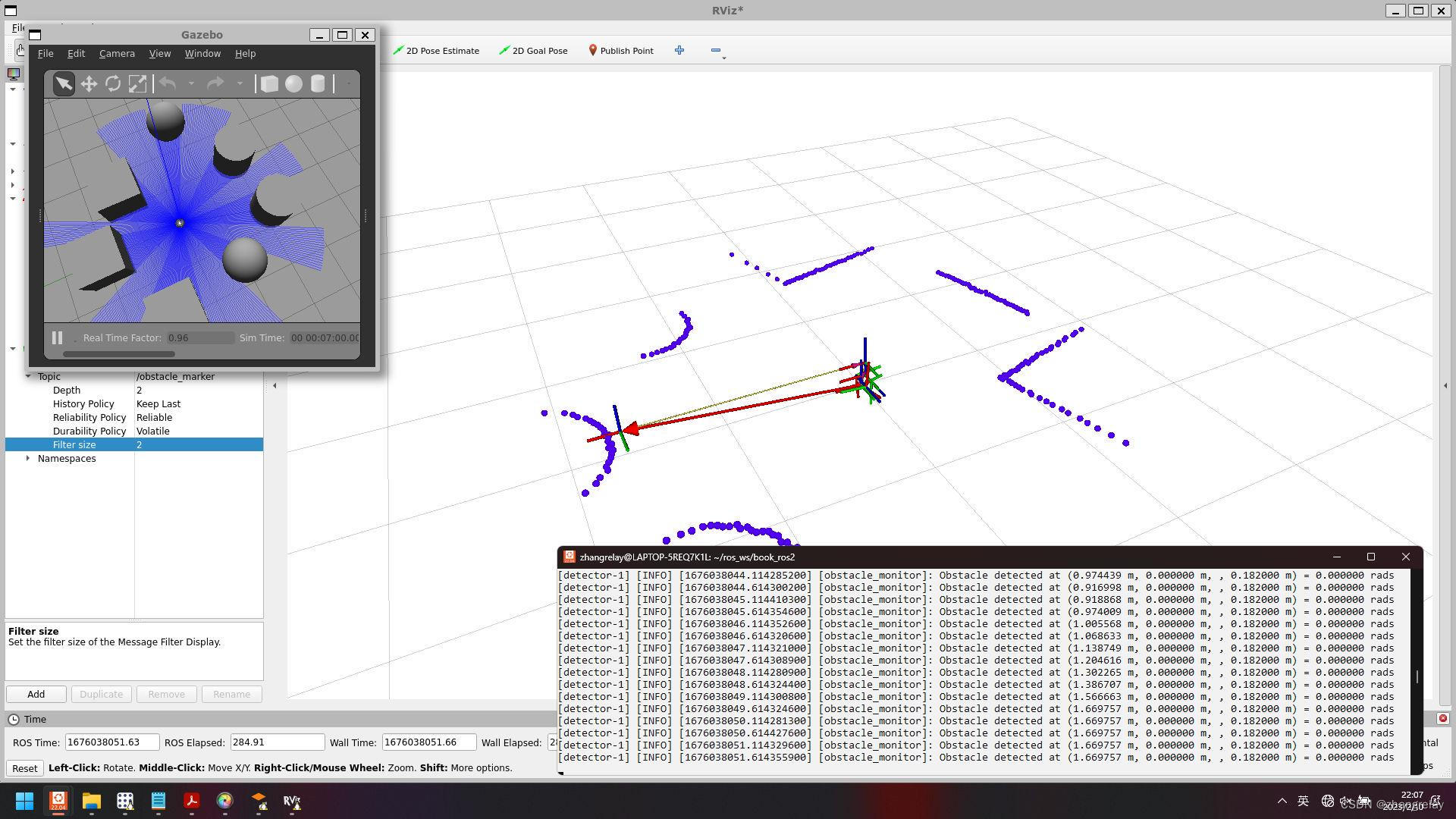
检测障碍物:
加个箭头→标记:
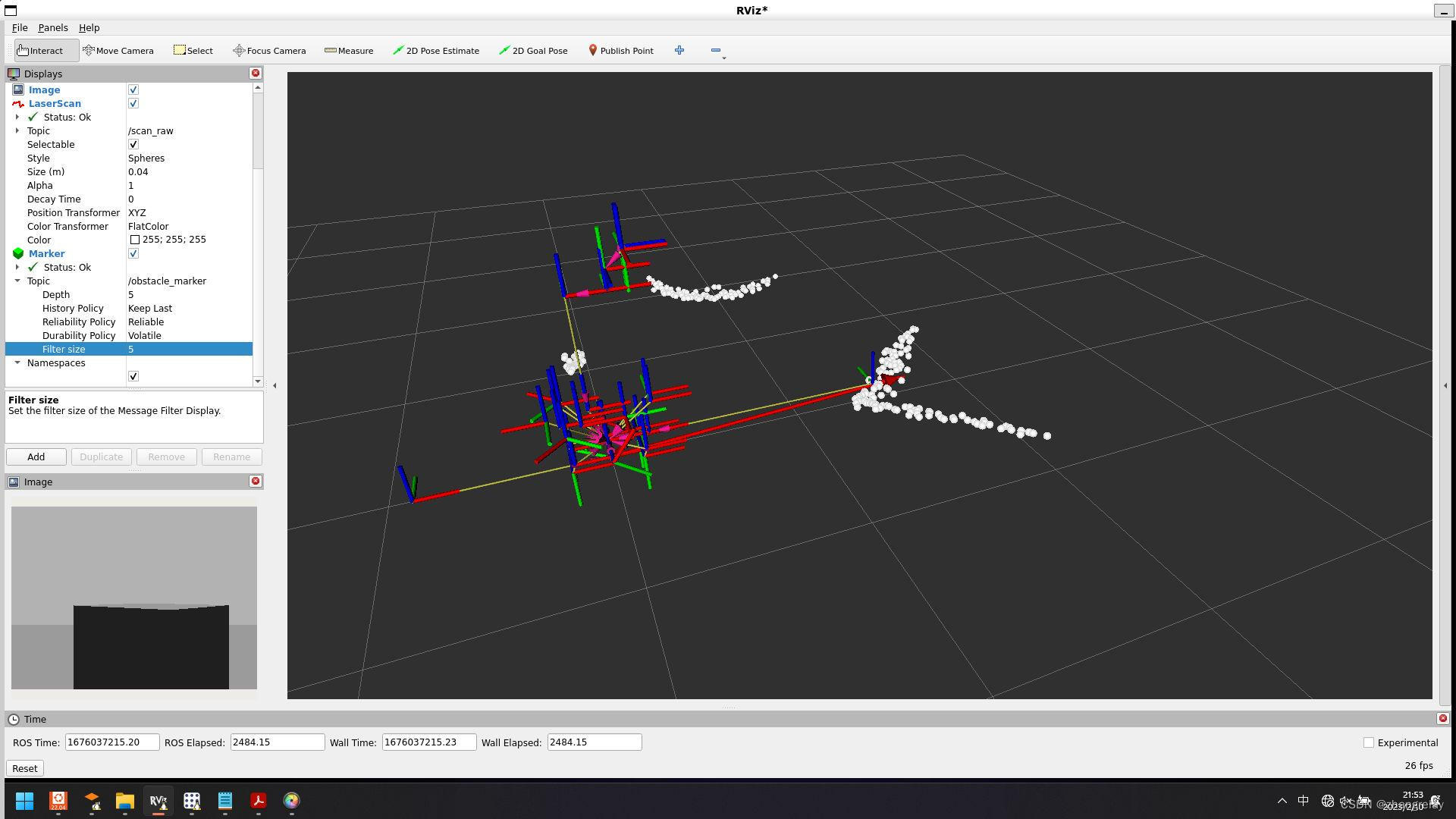
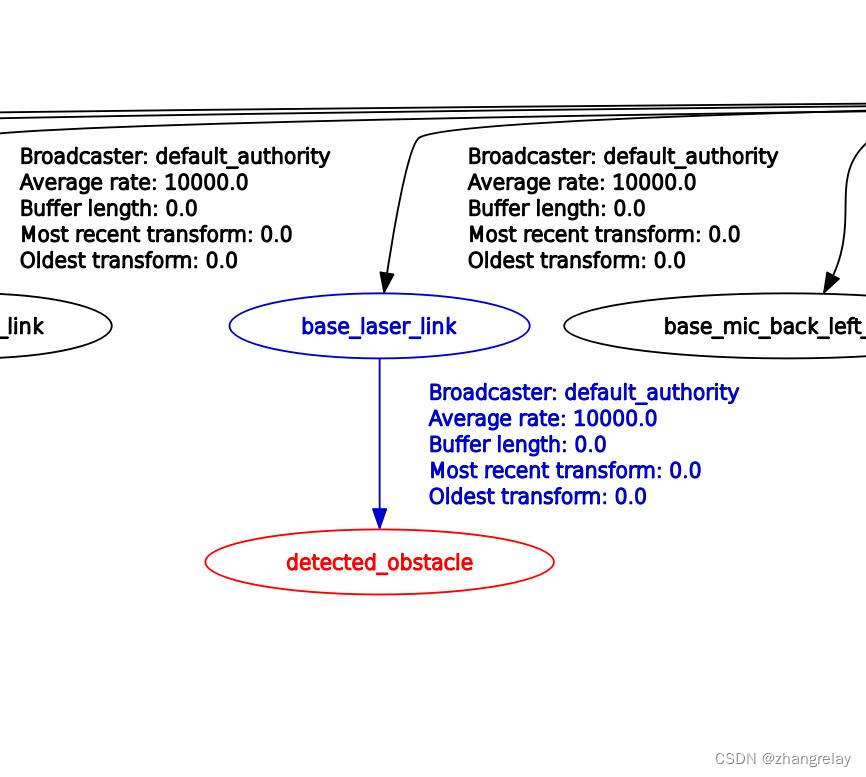
绘制 “base_footprint”, “detected_obstacle”:
-
// Copyright 2021 Intelligent Robotics Lab // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. #include <tf2/transform_datatypes.h> #include <tf2/LinearMath/Quaternion.h> #include <memory> #include "br2_tf2_detector/ObstacleMonitorNode.hpp" #include "geometry_msgs/msg/transform_stamped.hpp" #include "tf2_geometry_msgs/tf2_geometry_msgs.hpp" #include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp" namespace br2_tf2_detector { using namespace std::chrono_literals; ObstacleMonitorNode::ObstacleMonitorNode() : Node("obstacle_monitor"), tf_buffer_(), tf_listener_(tf_buffer_) { marker_pub_ = create_publisher<visualization_msgs::msg::Marker>("obstacle_marker", 1); timer_ = create_wall_timer( 500ms, std::bind(&ObstacleMonitorNode::control_cycle, this)); } void ObstacleMonitorNode::control_cycle() { geometry_msgs::msg::TransformStamped robot2obstacle; try { robot2obstacle = tf_buffer_.lookupTransform( "base_footprint", "detected_obstacle", tf2::TimePointZero); } catch (tf2::TransformException & ex) { RCLCPP_WARN(get_logger(), "Obstacle transform not found: %s", ex.what()); return; } double x = robot2obstacle.transform.translation.x; double y = robot2obstacle.transform.translation.y; double z = robot2obstacle.transform.translation.z; double theta = atan2(y, x); RCLCPP_INFO( get_logger(), "Obstacle detected at (%lf m, %lf m, , %lf m) = %lf rads", x, y, z, theta); visualization_msgs::msg::Marker obstacle_arrow; obstacle_arrow.header.frame_id = "base_footprint"; obstacle_arrow.header.stamp = now(); obstacle_arrow.type = visualization_msgs::msg::Marker::ARROW; obstacle_arrow.action = visualization_msgs::msg::Marker::ADD; obstacle_arrow.lifetime = rclcpp::Duration(1s); geometry_msgs::msg::Point start; start.x = 0.0; start.y = 0.0; start.z = 0.0; geometry_msgs::msg::Point end; end.x = x; end.y = y; end.z = z; obstacle_arrow.points = {start, end}; obstacle_arrow.color.r = 1.0; obstacle_arrow.color.g = 0.0; obstacle_arrow.color.b = 0.0; obstacle_arrow.color.a = 1.0; obstacle_arrow.scale.x = 0.02; obstacle_arrow.scale.y = 0.1; obstacle_arrow.scale.z = 0.1; marker_pub_->publish(obstacle_arrow); } } // namespace br2_tf2_detector
生成tf-detected_obstacle:
-
// Copyright 2021 Intelligent Robotics Lab // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. #include <memory> #include "br2_tf2_detector/ObstacleDetectorNode.hpp" #include "sensor_msgs/msg/laser_scan.hpp" #include "geometry_msgs/msg/transform_stamped.hpp" #include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp" namespace br2_tf2_detector { using std::placeholders::_1; ObstacleDetectorNode::ObstacleDetectorNode() : Node("obstacle_detector") { scan_sub_ = create_subscription<sensor_msgs::msg::LaserScan>( "input_scan", rclcpp::SensorDataQoS(), std::bind(&ObstacleDetectorNode::scan_callback, this, _1)); tf_broadcaster_ = std::make_shared<tf2_ros::StaticTransformBroadcaster>(*this); } void ObstacleDetectorNode::scan_callback(sensor_msgs::msg::LaserScan::UniquePtr msg) { double dist = msg->ranges[msg->ranges.size() / 2]; if (!std::isinf(dist)) { geometry_msgs::msg::TransformStamped detection_tf; detection_tf.header = msg->header; detection_tf.child_frame_id = "detected_obstacle"; detection_tf.transform.translation.x = msg->ranges[msg->ranges.size() / 2]; tf_broadcaster_->sendTransform(detection_tf); } } } // namespace br2_tf2_detector
scan重命名等:
-
# Copyright 2021 Intelligent Robotics Lab # # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. # You may obtain a copy of the License at # # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 # # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and # limitations under the License. from launch import LaunchDescription from launch_ros.actions import Node def generate_launch_description(): detector_cmd = Node(package='br2_tf2_detector', executable='detector', output='screen', parameters=[{ 'use_sim_time': True }], remappings=[ ('input_scan', '/scan_raw') ]) ld = LaunchDescription() ld.add_action(detector_cmd) return ld
remappings=[
(‘input_scan’, ‘/scan_raw’)
])
可以依据具体主题名称进行调整。
chatgpt:
要使用激光雷达数据,首先需要将激光雷达连接到你的机器人。然后,可以通过ROS2中的ROS2话题进行数据传输。激光雷达生成的数据通常是PointCloud2消息类型,该消息类型包含三维点的坐标信息。
接下来,可以通过创建一个ROS2节点来订阅并处理激光雷达生成的数据。您可以使用ROS2提供的函数,例如subscribe()和callback(),在该节点中实现这一点。回调函数可以访问接收到的数据,并对其进行处理。
最后,可以使用ROS2提供的函数,例如publish(),在该节点中发布处理后的数据,以便其他节点可以访问。
总而言之,使用ROS2中的激光雷达数据需要以下步骤:
连接激光雷达到机器人
通过ROS2话题传输数据
创建ROS2节点订阅和处理数据
在该节点中发布处理后的数据。
使用 ROS2 中的 tf2 库可以方便地处理坐标变换,包括平移和旋转。首先,需要安装 ROS2 中的 tf2 库,然后在代码中引入 tf2 的头文件。
接下来,需要创建一个 tf2 的 TransformBroadcaster 对象,它将负责广播坐标变换的数据。可以使用 TransformBroadcaster 对象的 sendTransform 函数来广播坐标变换的数据。
sendTransform 函数需要传入一些参数,例如:变换的时间戳、变换的原点坐标、变换的目标坐标、变换的平移量和旋转量。
最后,可以使用 tf2 的 TransformListener 对象来订阅坐标变换的数据。TransformListener 对象可以帮助计算从一个坐标系到另一个坐标系的变换。
以上是 ROS2 中使用 tf2 处理坐标数据的一般流程。详细的示例代码可以在 ROS2 官方文档中找到。



评论(0)
您还未登录,请登录后发表或查看评论