实现【sarsa】【Q-learning】算法路径规划任务 预期效果:到达绿色目标点
紫色为小车: 数学模型:[[np.cos(theta), 0],[np.sin(theta), 0],[0, 1.0]]
红色为障碍物: 碰撞:-5.0
绿色为目标区域: 到达:+2.0
其他奖励: 为了保证小车尽快到达目标区域,每step消耗0.02(奖励:-0.02)
距离奖励:奖励:(上一次距目标点距离-当前距目标点距离)*系数
输入:动作{0: 前进, 1: 左转, 2: 右转}
# 核心代码:
def _step(self, action):
self.last_state = np.copy(self.state)
self.state += self.dt * (self.get_f(self.state) + self.get_g(self.state) @ action) #根据小车模型进行计算下一状态
done = False #结束标志位
dist_goal = self._goal_dist() #到达目标的距离
reward = (self.last_goal_dist - dist_goal) #向着目标移动的奖励
self.last_goal_dist = dist_goal
info = dict()
if np.any(np.sum((self.state[:2] - self.hazards_locations_circle) ** 2, axis=1) < (
self.hazards_radius + self.car_size[1] / 2) ** 2): #与红色圆形障碍物发生碰撞
if 'cost' in info:
info['cost'] += 0.1
else:
info['cost'] = 0.1
self.state = self.last_state
reward += self.reward_obstacle
done = True
if np.any(np.sum((self.state[:2] - self.hazards_locations_line_disperse_1) ** 2, axis=1) < (
self.car_size[1] / 2) ** 2): #与墙壁1发生碰撞
if 'cost' in info:
info['cost'] += 0.1
else:
info['cost'] = 0.1
self.state = self.last_state
reward += self.reward_obstacle
done = True
if np.any(np.sum((self.state[:2] - self.hazards_locations_line_disperse_2) ** 2, axis=1) < (
self.car_size[1] / 2) ** 2): #与墙壁2发生碰撞
if 'cost' in info:
info['cost'] += 0.1
else:
info['cost'] = 0.1
self.state = self.last_state
reward += self.reward_obstacle
done = True
if np.abs(self.state[0]) > 3 or np.abs(self.state[1]) > 3: #跑出[3*3]的范围区域,即画面
self.state = self.last_state
reward += self.reward_obstacle
done = True
self.episode_step += 1
reward += self.reward_step_cost
# Check if goal is met
if self.goal_met(): # 到达目标
info['goal_met'] = True
reward += self.reward_goal # 目标点的奖励
done = True
if self.episode_step >= self.max_episode_steps: # 大于本轮最大步数
done = True
return self.state, reward, done, info
# 核心代码: def _step(self, action): self.last_state = np.copy(self.state) self.state += self.dt * (self.get_f(self.state) + self.get_g(self.state) @ action) #根据小车模型进行计算下一状态 done = False #结束标志位 dist_goal = self._goal_dist() #到达目标的距离 reward = (self.last_goal_dist - dist_goal) #向着目标移动的奖励 self.last_goal_dist = dist_goal info = dict() if np.any(np.sum((self.state[:2] - self.hazards_locations_circle) ** 2, axis=1) < ( self.hazards_radius + self.car_size[1] / 2) ** 2): #与红色圆形障碍物发生碰撞 if 'cost' in info: info['cost'] += 0.1 else: info['cost'] = 0.1 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True if np.any(np.sum((self.state[:2] - self.hazards_locations_line_disperse_1) ** 2, axis=1) < ( self.car_size[1] / 2) ** 2): #与墙壁1发生碰撞 if 'cost' in info: info['cost'] += 0.1 else: info['cost'] = 0.1 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True if np.any(np.sum((self.state[:2] - self.hazards_locations_line_disperse_2) ** 2, axis=1) < ( self.car_size[1] / 2) ** 2): #与墙壁2发生碰撞 if 'cost' in info: info['cost'] += 0.1 else: info['cost'] = 0.1 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True if np.abs(self.state[0]) > 3 or np.abs(self.state[1]) > 3: #跑出[3*3]的范围区域,即画面 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True self.episode_step += 1 reward += self.reward_step_cost # Check if goal is met if self.goal_met(): # 到达目标 info['goal_met'] = True reward += self.reward_goal # 目标点的奖励 done = True if self.episode_step >= self.max_episode_steps: # 大于本轮最大步数 done = True return self.state, reward, done, info
复制# 核心代码: def _step(self, action): self.last_state = np.copy(self.state) self.state += self.dt * (self.get_f(self.state) + self.get_g(self.state) @ action) #根据小车模型进行计算下一状态 done = False #结束标志位 dist_goal = self._goal_dist() #到达目标的距离 reward = (self.last_goal_dist - dist_goal) #向着目标移动的奖励 self.last_goal_dist = dist_goal info = dict() if np.any(np.sum((self.state[:2] - self.hazards_locations_circle) ** 2, axis=1) < ( self.hazards_radius + self.car_size[1] / 2) ** 2): #与红色圆形障碍物发生碰撞 if 'cost' in info: info['cost'] += 0.1 else: info['cost'] = 0.1 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True if np.any(np.sum((self.state[:2] - self.hazards_locations_line_disperse_1) ** 2, axis=1) < ( self.car_size[1] / 2) ** 2): #与墙壁1发生碰撞 if 'cost' in info: info['cost'] += 0.1 else: info['cost'] = 0.1 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True if np.any(np.sum((self.state[:2] - self.hazards_locations_line_disperse_2) ** 2, axis=1) < ( self.car_size[1] / 2) ** 2): #与墙壁2发生碰撞 if 'cost' in info: info['cost'] += 0.1 else: info['cost'] = 0.1 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True if np.abs(self.state[0]) > 3 or np.abs(self.state[1]) > 3: #跑出[3*3]的范围区域,即画面 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True self.episode_step += 1 reward += self.reward_step_cost # Check if goal is met if self.goal_met(): # 到达目标 info['goal_met'] = True reward += self.reward_goal # 目标点的奖励 done = True if self.episode_step >= self.max_episode_steps: # 大于本轮最大步数 done = True return self.state, reward, done, info
# 核心代码: def _step(self, action): self.last_state = np.copy(self.state) self.state += self.dt * (self.get_f(self.state) + self.get_g(self.state) @ action) #根据小车模型进行计算下一状态 done = False #结束标志位 dist_goal = self._goal_dist() #到达目标的距离 reward = (self.last_goal_dist - dist_goal) #向着目标移动的奖励 self.last_goal_dist = dist_goal info = dict() if np.any(np.sum((self.state[:2] - self.hazards_locations_circle) ** 2, axis=1) < ( self.hazards_radius + self.car_size[1] / 2) ** 2): #与红色圆形障碍物发生碰撞 if 'cost' in info: info['cost'] += 0.1 else: info['cost'] = 0.1 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True if np.any(np.sum((self.state[:2] - self.hazards_locations_line_disperse_1) ** 2, axis=1) < ( self.car_size[1] / 2) ** 2): #与墙壁1发生碰撞 if 'cost' in info: info['cost'] += 0.1 else: info['cost'] = 0.1 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True if np.any(np.sum((self.state[:2] - self.hazards_locations_line_disperse_2) ** 2, axis=1) < ( self.car_size[1] / 2) ** 2): #与墙壁2发生碰撞 if 'cost' in info: info['cost'] += 0.1 else: info['cost'] = 0.1 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True if np.abs(self.state[0]) > 3 or np.abs(self.state[1]) > 3: #跑出[3*3]的范围区域,即画面 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True self.episode_step += 1 reward += self.reward_step_cost # Check if goal is met if self.goal_met(): # 到达目标 info['goal_met'] = True reward += self.reward_goal # 目标点的奖励 done = True if self.episode_step >= self.max_episode_steps: # 大于本轮最大步数 done = True return self.state, reward, done, info
# 核心代码: def _step(self, action): self.last_state = np.copy(self.state) self.state += self.dt * (self.get_f(self.state) + self.get_g(self.state) @ action) #根据小车模型进行计算下一状态 done = False #结束标志位 dist_goal = self._goal_dist() #到达目标的距离 reward = (self.last_goal_dist - dist_goal) #向着目标移动的奖励 self.last_goal_dist = dist_goal info = dict() if np.any(np.sum((self.state[:2] - self.hazards_locations_circle) ** 2, axis=1) < ( self.hazards_radius + self.car_size[1] / 2) ** 2): #与红色圆形障碍物发生碰撞 if 'cost' in info: info['cost'] += 0.1 else: info['cost'] = 0.1 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True if np.any(np.sum((self.state[:2] - self.hazards_locations_line_disperse_1) ** 2, axis=1) < ( self.car_size[1] / 2) ** 2): #与墙壁1发生碰撞 if 'cost' in info: info['cost'] += 0.1 else: info['cost'] = 0.1 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True if np.any(np.sum((self.state[:2] - self.hazards_locations_line_disperse_2) ** 2, axis=1) < ( self.car_size[1] / 2) ** 2): #与墙壁2发生碰撞 if 'cost' in info: info['cost'] += 0.1 else: info['cost'] = 0.1 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True if np.abs(self.state[0]) > 3 or np.abs(self.state[1]) > 3: #跑出[3*3]的范围区域,即画面 self.state = self.last_state reward += self.reward_obstacle done = True self.episode_step += 1 reward += self.reward_step_cost # Check if goal is met if self.goal_met(): # 到达目标 info['goal_met'] = True reward += self.reward_goal # 目标点的奖励 done = True if self.episode_step >= self.max_episode_steps: # 大于本轮最大步数 done = True return self.state, reward, done, info
!pip install gym matplotlib pygame!pip install gym matplotlib pygame
复制!pip install gym matplotlib pygame
import gym
import numpy as np
import time
from envs.unicycle_env import UnicycleEnv
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
import gym import numpy as np import time from envs.unicycle_env import UnicycleEnv import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.patches as patches
复制import gym import numpy as np import time from envs.unicycle_env import UnicycleEnv import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.patches as patches
import gym import numpy as np import time from envs.unicycle_env import UnicycleEnv import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.patches as patches
import gym import numpy as np import time from envs.unicycle_env import UnicycleEnv import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.patches as patches
SARSA 和 Q-learning 都是强化学习中常见的算法。它们的目标都是学习表格 ,来指导智能体在环境中做出决策。
两种算法的区别在于它们对于未来奖励的处理方式:
Q-learning 是一种 off-policy 的算法,它会选择当前状态下最大 Q 值对应的动作作为决策。
Q值 更新方式:
而 SARSA 则是一种 on-policy 的算法,它会在当前状态下按照某种策略选择一个动作,然后在下一个状态下再按照相同的策略选择动作,并根据这个过程计算出一个 Q 值。
Q值 更新方式:
Q-learning 更侧重于学习最大化的长期奖励,而 SARSA 更侧重于学习按照某个策略的短期奖励。
复制 这里是两种算法sarsa与Q-learning的代码实现
#Sarsa算法实现
class SarsaAgent(object):
def __init__(self, obs_n, act_n, learning_rate=0.01, gamma=0.9, epsilon_coefficient=0.5):
self.act_n = act_n # 动作维度,有几个动作可选
self.lr = learning_rate # 学习率
self.gamma = gamma # reward的衰减率
self.epsilon_coefficient = epsilon_coefficient # 按一定概率随机选动作
self.Q = np.zeros((obs_n, act_n))
# 根据输入观察值,采样输出的动作值,带探索
def sample(self, obs, episode):
self.epsilon = self.epsilon_coefficient * (0.98 ** episode)
if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < (1.0 - self.epsilon): # 根据table的Q值选动作
action = self.predict(obs)
else:
action = np.random.choice(self.act_n) # 有一定概率随机探索选取一个动作
return action
# 根据输入观察值,预测输出的动作值
def predict(self, obs):
Q_list = self.Q[obs, :]
maxQ = np.max(Q_list)
action_list = np.where(Q_list == maxQ)[0] # maxQ可能对应多个action
action = np.random.choice(action_list)
return action
# 学习方法,也就是更新Q-table的方法
def learn(self, obs, action, reward, next_obs, next_action, done):
predict_Q = self.Q[obs, action]
if done:
target_Q = reward # 没有下一个状态了
else:
target_Q = reward + self.gamma * self.Q[next_obs, next_action] # Sarsa
self.Q[obs, action] += self.lr * (target_Q - predict_Q) # 修正q
# 保存Q表格数据到文件
def save(self):
npy_file = './q_table_sarsa.npy'
np.save(npy_file, self.Q)
# 从文件中读取数据到Q表格中
def restore(self, npy_file='./q_table_sarsa.npy'):
self.Q = np.load(npy_file)
#Sarsa算法实现 class SarsaAgent(object): def __init__(self, obs_n, act_n, learning_rate=0.01, gamma=0.9, epsilon_coefficient=0.5): self.act_n = act_n # 动作维度,有几个动作可选 self.lr = learning_rate # 学习率 self.gamma = gamma # reward的衰减率 self.epsilon_coefficient = epsilon_coefficient # 按一定概率随机选动作 self.Q = np.zeros((obs_n, act_n)) # 根据输入观察值,采样输出的动作值,带探索 def sample(self, obs, episode): self.epsilon = self.epsilon_coefficient * (0.98 ** episode) if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < (1.0 - self.epsilon): # 根据table的Q值选动作 action = self.predict(obs) else: action = np.random.choice(self.act_n) # 有一定概率随机探索选取一个动作 return action # 根据输入观察值,预测输出的动作值 def predict(self, obs): Q_list = self.Q[obs, :] maxQ = np.max(Q_list) action_list = np.where(Q_list == maxQ)[0] # maxQ可能对应多个action action = np.random.choice(action_list) return action # 学习方法,也就是更新Q-table的方法 def learn(self, obs, action, reward, next_obs, next_action, done): predict_Q = self.Q[obs, action] if done: target_Q = reward # 没有下一个状态了 else: target_Q = reward + self.gamma * self.Q[next_obs, next_action] # Sarsa self.Q[obs, action] += self.lr * (target_Q - predict_Q) # 修正q # 保存Q表格数据到文件 def save(self): npy_file = './q_table_sarsa.npy' np.save(npy_file, self.Q) # 从文件中读取数据到Q表格中 def restore(self, npy_file='./q_table_sarsa.npy'): self.Q = np.load(npy_file)
复制#Sarsa算法实现 class SarsaAgent(object): def __init__(self, obs_n, act_n, learning_rate=0.01, gamma=0.9, epsilon_coefficient=0.5): self.act_n = act_n # 动作维度,有几个动作可选 self.lr = learning_rate # 学习率 self.gamma = gamma # reward的衰减率 self.epsilon_coefficient = epsilon_coefficient # 按一定概率随机选动作 self.Q = np.zeros((obs_n, act_n)) # 根据输入观察值,采样输出的动作值,带探索 def sample(self, obs, episode): self.epsilon = self.epsilon_coefficient * (0.98 ** episode) if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < (1.0 - self.epsilon): # 根据table的Q值选动作 action = self.predict(obs) else: action = np.random.choice(self.act_n) # 有一定概率随机探索选取一个动作 return action # 根据输入观察值,预测输出的动作值 def predict(self, obs): Q_list = self.Q[obs, :] maxQ = np.max(Q_list) action_list = np.where(Q_list == maxQ)[0] # maxQ可能对应多个action action = np.random.choice(action_list) return action # 学习方法,也就是更新Q-table的方法 def learn(self, obs, action, reward, next_obs, next_action, done): predict_Q = self.Q[obs, action] if done: target_Q = reward # 没有下一个状态了 else: target_Q = reward + self.gamma * self.Q[next_obs, next_action] # Sarsa self.Q[obs, action] += self.lr * (target_Q - predict_Q) # 修正q # 保存Q表格数据到文件 def save(self): npy_file = './q_table_sarsa.npy' np.save(npy_file, self.Q) # 从文件中读取数据到Q表格中 def restore(self, npy_file='./q_table_sarsa.npy'): self.Q = np.load(npy_file)
#Sarsa算法实现 class SarsaAgent(object): def __init__(self, obs_n, act_n, learning_rate=0.01, gamma=0.9, epsilon_coefficient=0.5): self.act_n = act_n # 动作维度,有几个动作可选 self.lr = learning_rate # 学习率 self.gamma = gamma # reward的衰减率 self.epsilon_coefficient = epsilon_coefficient # 按一定概率随机选动作 self.Q = np.zeros((obs_n, act_n)) # 根据输入观察值,采样输出的动作值,带探索 def sample(self, obs, episode): self.epsilon = self.epsilon_coefficient * (0.98 ** episode) if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < (1.0 - self.epsilon): # 根据table的Q值选动作 action = self.predict(obs) else: action = np.random.choice(self.act_n) # 有一定概率随机探索选取一个动作 return action # 根据输入观察值,预测输出的动作值 def predict(self, obs): Q_list = self.Q[obs, :] maxQ = np.max(Q_list) action_list = np.where(Q_list == maxQ)[0] # maxQ可能对应多个action action = np.random.choice(action_list) return action # 学习方法,也就是更新Q-table的方法 def learn(self, obs, action, reward, next_obs, next_action, done): predict_Q = self.Q[obs, action] if done: target_Q = reward # 没有下一个状态了 else: target_Q = reward + self.gamma * self.Q[next_obs, next_action] # Sarsa self.Q[obs, action] += self.lr * (target_Q - predict_Q) # 修正q # 保存Q表格数据到文件 def save(self): npy_file = './q_table_sarsa.npy' np.save(npy_file, self.Q) # 从文件中读取数据到Q表格中 def restore(self, npy_file='./q_table_sarsa.npy'): self.Q = np.load(npy_file)
#Sarsa算法实现 class SarsaAgent(object): def __init__(self, obs_n, act_n, learning_rate=0.01, gamma=0.9, epsilon_coefficient=0.5): self.act_n = act_n # 动作维度,有几个动作可选 self.lr = learning_rate # 学习率 self.gamma = gamma # reward的衰减率 self.epsilon_coefficient = epsilon_coefficient # 按一定概率随机选动作 self.Q = np.zeros((obs_n, act_n)) # 根据输入观察值,采样输出的动作值,带探索 def sample(self, obs, episode): self.epsilon = self.epsilon_coefficient * (0.98 ** episode) if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < (1.0 - self.epsilon): # 根据table的Q值选动作 action = self.predict(obs) else: action = np.random.choice(self.act_n) # 有一定概率随机探索选取一个动作 return action # 根据输入观察值,预测输出的动作值 def predict(self, obs): Q_list = self.Q[obs, :] maxQ = np.max(Q_list) action_list = np.where(Q_list == maxQ)[0] # maxQ可能对应多个action action = np.random.choice(action_list) return action # 学习方法,也就是更新Q-table的方法 def learn(self, obs, action, reward, next_obs, next_action, done): predict_Q = self.Q[obs, action] if done: target_Q = reward # 没有下一个状态了 else: target_Q = reward + self.gamma * self.Q[next_obs, next_action] # Sarsa self.Q[obs, action] += self.lr * (target_Q - predict_Q) # 修正q # 保存Q表格数据到文件 def save(self): npy_file = './q_table_sarsa.npy' np.save(npy_file, self.Q) # 从文件中读取数据到Q表格中 def restore(self, npy_file='./q_table_sarsa.npy'): self.Q = np.load(npy_file)
#QLearning算法实现
class QLearningAgent(object):
def __init__(self, obs_n, act_n, learning_rate=0.01, gamma=0.9, epsilon_coefficient=0.5):
self.act_n = act_n # 动作维度,有几个动作可选
self.lr = learning_rate # 学习率
self.gamma = gamma # reward的衰减率
self.epsilon_coefficient = epsilon_coefficient # 按一定概率随机选动作
self.Q = np.zeros((obs_n, act_n))
# 根据输入观察值,采样输出的动作值,带探索
def sample(self, obs, episode):
self.epsilon = self.epsilon_coefficient * (0.98 ** episode)
if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < (1.0 - self.epsilon): # 根据table的Q值选动作
action = self.predict(obs)
else:
action = np.random.choice(self.act_n) # 有一定概率随机探索选取一个动作
return action
# 根据输入观察值,预测输出的动作值
def predict(self, obs):
Q_list = self.Q[obs, :]
maxQ = np.max(Q_list)
action_list = np.where(Q_list == maxQ)[0] # maxQ可能对应多个action
action = np.random.choice(action_list)
return action
# 学习方法,也就是更新Q-table的方法
def learn(self, obs, action, reward, next_obs, done):
predict_Q = self.Q[obs, action]
if done:
target_Q = reward # 没有下一个状态了
else:
target_Q = reward + self.gamma * np.max(self.Q[next_obs, :]) # Q-learning
self.Q[obs, action] += self.lr * (target_Q - predict_Q) # 修正q
# 保存Q表格数据到文件
def save(self):
npy_file = './q_table_qlearning.npy'
np.save(npy_file, self.Q)
# 从文件中读取数据到Q表格中
def restore(self, npy_file='./q_table_qlearning.npy'):
self.Q = np.load(npy_file)
#QLearning算法实现 class QLearningAgent(object): def __init__(self, obs_n, act_n, learning_rate=0.01, gamma=0.9, epsilon_coefficient=0.5): self.act_n = act_n # 动作维度,有几个动作可选 self.lr = learning_rate # 学习率 self.gamma = gamma # reward的衰减率 self.epsilon_coefficient = epsilon_coefficient # 按一定概率随机选动作 self.Q = np.zeros((obs_n, act_n)) # 根据输入观察值,采样输出的动作值,带探索 def sample(self, obs, episode): self.epsilon = self.epsilon_coefficient * (0.98 ** episode) if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < (1.0 - self.epsilon): # 根据table的Q值选动作 action = self.predict(obs) else: action = np.random.choice(self.act_n) # 有一定概率随机探索选取一个动作 return action # 根据输入观察值,预测输出的动作值 def predict(self, obs): Q_list = self.Q[obs, :] maxQ = np.max(Q_list) action_list = np.where(Q_list == maxQ)[0] # maxQ可能对应多个action action = np.random.choice(action_list) return action # 学习方法,也就是更新Q-table的方法 def learn(self, obs, action, reward, next_obs, done): predict_Q = self.Q[obs, action] if done: target_Q = reward # 没有下一个状态了 else: target_Q = reward + self.gamma * np.max(self.Q[next_obs, :]) # Q-learning self.Q[obs, action] += self.lr * (target_Q - predict_Q) # 修正q # 保存Q表格数据到文件 def save(self): npy_file = './q_table_qlearning.npy' np.save(npy_file, self.Q) # 从文件中读取数据到Q表格中 def restore(self, npy_file='./q_table_qlearning.npy'): self.Q = np.load(npy_file)
复制#QLearning算法实现 class QLearningAgent(object): def __init__(self, obs_n, act_n, learning_rate=0.01, gamma=0.9, epsilon_coefficient=0.5): self.act_n = act_n # 动作维度,有几个动作可选 self.lr = learning_rate # 学习率 self.gamma = gamma # reward的衰减率 self.epsilon_coefficient = epsilon_coefficient # 按一定概率随机选动作 self.Q = np.zeros((obs_n, act_n)) # 根据输入观察值,采样输出的动作值,带探索 def sample(self, obs, episode): self.epsilon = self.epsilon_coefficient * (0.98 ** episode) if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < (1.0 - self.epsilon): # 根据table的Q值选动作 action = self.predict(obs) else: action = np.random.choice(self.act_n) # 有一定概率随机探索选取一个动作 return action # 根据输入观察值,预测输出的动作值 def predict(self, obs): Q_list = self.Q[obs, :] maxQ = np.max(Q_list) action_list = np.where(Q_list == maxQ)[0] # maxQ可能对应多个action action = np.random.choice(action_list) return action # 学习方法,也就是更新Q-table的方法 def learn(self, obs, action, reward, next_obs, done): predict_Q = self.Q[obs, action] if done: target_Q = reward # 没有下一个状态了 else: target_Q = reward + self.gamma * np.max(self.Q[next_obs, :]) # Q-learning self.Q[obs, action] += self.lr * (target_Q - predict_Q) # 修正q # 保存Q表格数据到文件 def save(self): npy_file = './q_table_qlearning.npy' np.save(npy_file, self.Q) # 从文件中读取数据到Q表格中 def restore(self, npy_file='./q_table_qlearning.npy'): self.Q = np.load(npy_file)
#QLearning算法实现 class QLearningAgent(object): def __init__(self, obs_n, act_n, learning_rate=0.01, gamma=0.9, epsilon_coefficient=0.5): self.act_n = act_n # 动作维度,有几个动作可选 self.lr = learning_rate # 学习率 self.gamma = gamma # reward的衰减率 self.epsilon_coefficient = epsilon_coefficient # 按一定概率随机选动作 self.Q = np.zeros((obs_n, act_n)) # 根据输入观察值,采样输出的动作值,带探索 def sample(self, obs, episode): self.epsilon = self.epsilon_coefficient * (0.98 ** episode) if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < (1.0 - self.epsilon): # 根据table的Q值选动作 action = self.predict(obs) else: action = np.random.choice(self.act_n) # 有一定概率随机探索选取一个动作 return action # 根据输入观察值,预测输出的动作值 def predict(self, obs): Q_list = self.Q[obs, :] maxQ = np.max(Q_list) action_list = np.where(Q_list == maxQ)[0] # maxQ可能对应多个action action = np.random.choice(action_list) return action # 学习方法,也就是更新Q-table的方法 def learn(self, obs, action, reward, next_obs, done): predict_Q = self.Q[obs, action] if done: target_Q = reward # 没有下一个状态了 else: target_Q = reward + self.gamma * np.max(self.Q[next_obs, :]) # Q-learning self.Q[obs, action] += self.lr * (target_Q - predict_Q) # 修正q # 保存Q表格数据到文件 def save(self): npy_file = './q_table_qlearning.npy' np.save(npy_file, self.Q) # 从文件中读取数据到Q表格中 def restore(self, npy_file='./q_table_qlearning.npy'): self.Q = np.load(npy_file)
#QLearning算法实现 class QLearningAgent(object): def __init__(self, obs_n, act_n, learning_rate=0.01, gamma=0.9, epsilon_coefficient=0.5): self.act_n = act_n # 动作维度,有几个动作可选 self.lr = learning_rate # 学习率 self.gamma = gamma # reward的衰减率 self.epsilon_coefficient = epsilon_coefficient # 按一定概率随机选动作 self.Q = np.zeros((obs_n, act_n)) # 根据输入观察值,采样输出的动作值,带探索 def sample(self, obs, episode): self.epsilon = self.epsilon_coefficient * (0.98 ** episode) if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < (1.0 - self.epsilon): # 根据table的Q值选动作 action = self.predict(obs) else: action = np.random.choice(self.act_n) # 有一定概率随机探索选取一个动作 return action # 根据输入观察值,预测输出的动作值 def predict(self, obs): Q_list = self.Q[obs, :] maxQ = np.max(Q_list) action_list = np.where(Q_list == maxQ)[0] # maxQ可能对应多个action action = np.random.choice(action_list) return action # 学习方法,也就是更新Q-table的方法 def learn(self, obs, action, reward, next_obs, done): predict_Q = self.Q[obs, action] if done: target_Q = reward # 没有下一个状态了 else: target_Q = reward + self.gamma * np.max(self.Q[next_obs, :]) # Q-learning self.Q[obs, action] += self.lr * (target_Q - predict_Q) # 修正q # 保存Q表格数据到文件 def save(self): npy_file = './q_table_qlearning.npy' np.save(npy_file, self.Q) # 从文件中读取数据到Q表格中 def restore(self, npy_file='./q_table_qlearning.npy'): self.Q = np.load(npy_file)
def run_episode(env, agent, episode, render=False):
total_steps = 0 # 记录每个episode走了多少step
total_reward = 0
obs = env.reset() # 重置环境, 重新开一局(即开始新的一个episode)
while True:
action = agent.sample(obs, episode) # 根据算法选择一个动作
next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) # 与环境进行一个交互
# 训练 Q-learning算法
agent.learn(obs, action, reward, next_obs, done)
obs = next_obs # 存储上一个观察值
total_reward += reward
total_steps += 1 # 计算step数
if render:
env.render() # 渲染新的一帧图形
if done:
break
return total_reward, total_steps
def test_Q_episode(env, agent, draw=False, render=False):
total_reward = 0
obs = env.reset()
trajectory_list = []
Qframes = []
while True:
action = agent.predict(obs) # greedy
next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
total_reward += reward
obs = next_obs
if render:
Qframes.append(env.render(mode='rgb_array'))
if done:
break
trajectory_list.append(np.array([next_obs / 70, next_obs % 70]))
trajectory_array = np.array(trajectory_list)
if draw:
plt.plot(trajectory_array[:, 0], trajectory_array[:, 1])
plt.show()
# Qdisplay_frames_as_gif(Qframes, 'qlearning.gif')
return total_reward, trajectory_array
def show_Q_traj(env, agent):
total_reward = 0
obs = env.reset()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
for i in range(len(env.hazards_locations_circle)):
ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.hazards_locations_circle[i], env.hazards_radius, color='r'))
ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g'))
ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g'))
line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[0][0], env.hazards_locations_line[0][1]),
(env.hazards_locations_line[1][0], env.hazards_locations_line[1][1]), "data", "data",
color='r', linewidth=5)
ax.add_patch(line)
line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[2][0], env.hazards_locations_line[2][1]),
(env.hazards_locations_line[3][0], env.hazards_locations_line[3][1]), "data", "data",
color='r', linewidth=5)
ax.add_patch(line)
car_width = 0.4
car_height = 0.3
pose = env.get_pose()
car = plt.Rectangle(([pose[0] - 0.2, pose[1] - 0.15]), 0.4, 0.3, angle=np.rad2deg(pose[4]))
ax.add_patch(car)
p_theta = plt.quiver(pose[0], pose[1], pose[0] + .3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) # 箭头
plt.xlim([-3.0, 3.0])
plt.ylim([-3.0, 3.0])
ax.set_aspect('equal', 'box')
x_positions = []
y_positions = []
start_time = time.time()
while True:
car_center = (pose[0], pose[1])
rect_x = car_center[0] - (car_width / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) + (car_height / 2) * np.sin(pose[4])
rect_y = car_center[1] - (car_height / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) - (car_width / 2) * np.sin(pose[4])
# 设置矩形的新位置和角度
car.set_xy((rect_x, rect_y))
x_positions.append(pose[0])
y_positions.append(pose[1])
car.angle = np.rad2deg(pose[4])
p_theta.XY[:, 0] = pose[0]
p_theta.XY[:, 1] = pose[1]
p_theta.set_UVC(.3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3])
step_time_start = time.time()
action = agent.predict(obs)
single_step_time = time.time() - step_time_start
next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
pose = env.get_pose()
total_reward += reward
obs = next_obs
plt.plot(x_positions, y_positions)
if done:
delta_time = time.time() - start_time
break
plt.title('QLearning算法轨迹图')
plt.savefig('Q_traj.png', dpi=300)
return env.dist_2_goal, env.travel_dist, env.episode_step, delta_time, single_step_time
from matplotlib import animation
def Qdisplay_frames_as_gif(frames, file_name):
patch = plt.imshow(frames[0])
plt.axis('off')
def animate(i):
patch.set_data(frames[i])
anim = animation.FuncAnimation(plt.gcf(), animate, frames=len(frames), interval=5)
anim.save(file_name, writer='pillow', fps=30)
def run_episode(env, agent, episode, render=False): total_steps = 0 # 记录每个episode走了多少step total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() # 重置环境, 重新开一局(即开始新的一个episode) while True: action = agent.sample(obs, episode) # 根据算法选择一个动作 next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) # 与环境进行一个交互 # 训练 Q-learning算法 agent.learn(obs, action, reward, next_obs, done) obs = next_obs # 存储上一个观察值 total_reward += reward total_steps += 1 # 计算step数 if render: env.render() # 渲染新的一帧图形 if done: break return total_reward, total_steps def test_Q_episode(env, agent, draw=False, render=False): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() trajectory_list = [] Qframes = [] while True: action = agent.predict(obs) # greedy next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) total_reward += reward obs = next_obs if render: Qframes.append(env.render(mode='rgb_array')) if done: break trajectory_list.append(np.array([next_obs / 70, next_obs % 70])) trajectory_array = np.array(trajectory_list) if draw: plt.plot(trajectory_array[:, 0], trajectory_array[:, 1]) plt.show() # Qdisplay_frames_as_gif(Qframes, 'qlearning.gif') return total_reward, trajectory_array def show_Q_traj(env, agent): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() fig, ax = plt.subplots() for i in range(len(env.hazards_locations_circle)): ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.hazards_locations_circle[i], env.hazards_radius, color='r')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[0][0], env.hazards_locations_line[0][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[1][0], env.hazards_locations_line[1][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[2][0], env.hazards_locations_line[2][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[3][0], env.hazards_locations_line[3][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) car_width = 0.4 car_height = 0.3 pose = env.get_pose() car = plt.Rectangle(([pose[0] - 0.2, pose[1] - 0.15]), 0.4, 0.3, angle=np.rad2deg(pose[4])) ax.add_patch(car) p_theta = plt.quiver(pose[0], pose[1], pose[0] + .3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) # 箭头 plt.xlim([-3.0, 3.0]) plt.ylim([-3.0, 3.0]) ax.set_aspect('equal', 'box') x_positions = [] y_positions = [] start_time = time.time() while True: car_center = (pose[0], pose[1]) rect_x = car_center[0] - (car_width / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) + (car_height / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) rect_y = car_center[1] - (car_height / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) - (car_width / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) # 设置矩形的新位置和角度 car.set_xy((rect_x, rect_y)) x_positions.append(pose[0]) y_positions.append(pose[1]) car.angle = np.rad2deg(pose[4]) p_theta.XY[:, 0] = pose[0] p_theta.XY[:, 1] = pose[1] p_theta.set_UVC(.3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) step_time_start = time.time() action = agent.predict(obs) single_step_time = time.time() - step_time_start next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) pose = env.get_pose() total_reward += reward obs = next_obs plt.plot(x_positions, y_positions) if done: delta_time = time.time() - start_time break plt.title('QLearning算法轨迹图') plt.savefig('Q_traj.png', dpi=300) return env.dist_2_goal, env.travel_dist, env.episode_step, delta_time, single_step_time from matplotlib import animation def Qdisplay_frames_as_gif(frames, file_name): patch = plt.imshow(frames[0]) plt.axis('off') def animate(i): patch.set_data(frames[i]) anim = animation.FuncAnimation(plt.gcf(), animate, frames=len(frames), interval=5) anim.save(file_name, writer='pillow', fps=30)
复制def run_episode(env, agent, episode, render=False): total_steps = 0 # 记录每个episode走了多少step total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() # 重置环境, 重新开一局(即开始新的一个episode) while True: action = agent.sample(obs, episode) # 根据算法选择一个动作 next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) # 与环境进行一个交互 # 训练 Q-learning算法 agent.learn(obs, action, reward, next_obs, done) obs = next_obs # 存储上一个观察值 total_reward += reward total_steps += 1 # 计算step数 if render: env.render() # 渲染新的一帧图形 if done: break return total_reward, total_steps def test_Q_episode(env, agent, draw=False, render=False): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() trajectory_list = [] Qframes = [] while True: action = agent.predict(obs) # greedy next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) total_reward += reward obs = next_obs if render: Qframes.append(env.render(mode='rgb_array')) if done: break trajectory_list.append(np.array([next_obs / 70, next_obs % 70])) trajectory_array = np.array(trajectory_list) if draw: plt.plot(trajectory_array[:, 0], trajectory_array[:, 1]) plt.show() # Qdisplay_frames_as_gif(Qframes, 'qlearning.gif') return total_reward, trajectory_array def show_Q_traj(env, agent): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() fig, ax = plt.subplots() for i in range(len(env.hazards_locations_circle)): ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.hazards_locations_circle[i], env.hazards_radius, color='r')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[0][0], env.hazards_locations_line[0][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[1][0], env.hazards_locations_line[1][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[2][0], env.hazards_locations_line[2][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[3][0], env.hazards_locations_line[3][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) car_width = 0.4 car_height = 0.3 pose = env.get_pose() car = plt.Rectangle(([pose[0] - 0.2, pose[1] - 0.15]), 0.4, 0.3, angle=np.rad2deg(pose[4])) ax.add_patch(car) p_theta = plt.quiver(pose[0], pose[1], pose[0] + .3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) # 箭头 plt.xlim([-3.0, 3.0]) plt.ylim([-3.0, 3.0]) ax.set_aspect('equal', 'box') x_positions = [] y_positions = [] start_time = time.time() while True: car_center = (pose[0], pose[1]) rect_x = car_center[0] - (car_width / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) + (car_height / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) rect_y = car_center[1] - (car_height / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) - (car_width / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) # 设置矩形的新位置和角度 car.set_xy((rect_x, rect_y)) x_positions.append(pose[0]) y_positions.append(pose[1]) car.angle = np.rad2deg(pose[4]) p_theta.XY[:, 0] = pose[0] p_theta.XY[:, 1] = pose[1] p_theta.set_UVC(.3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) step_time_start = time.time() action = agent.predict(obs) single_step_time = time.time() - step_time_start next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) pose = env.get_pose() total_reward += reward obs = next_obs plt.plot(x_positions, y_positions) if done: delta_time = time.time() - start_time break plt.title('QLearning算法轨迹图') plt.savefig('Q_traj.png', dpi=300) return env.dist_2_goal, env.travel_dist, env.episode_step, delta_time, single_step_time from matplotlib import animation def Qdisplay_frames_as_gif(frames, file_name): patch = plt.imshow(frames[0]) plt.axis('off') def animate(i): patch.set_data(frames[i]) anim = animation.FuncAnimation(plt.gcf(), animate, frames=len(frames), interval=5) anim.save(file_name, writer='pillow', fps=30)
def run_episode(env, agent, episode, render=False): total_steps = 0 # 记录每个episode走了多少step total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() # 重置环境, 重新开一局(即开始新的一个episode) while True: action = agent.sample(obs, episode) # 根据算法选择一个动作 next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) # 与环境进行一个交互 # 训练 Q-learning算法 agent.learn(obs, action, reward, next_obs, done) obs = next_obs # 存储上一个观察值 total_reward += reward total_steps += 1 # 计算step数 if render: env.render() # 渲染新的一帧图形 if done: break return total_reward, total_steps def test_Q_episode(env, agent, draw=False, render=False): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() trajectory_list = [] Qframes = [] while True: action = agent.predict(obs) # greedy next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) total_reward += reward obs = next_obs if render: Qframes.append(env.render(mode='rgb_array')) if done: break trajectory_list.append(np.array([next_obs / 70, next_obs % 70])) trajectory_array = np.array(trajectory_list) if draw: plt.plot(trajectory_array[:, 0], trajectory_array[:, 1]) plt.show() # Qdisplay_frames_as_gif(Qframes, 'qlearning.gif') return total_reward, trajectory_array def show_Q_traj(env, agent): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() fig, ax = plt.subplots() for i in range(len(env.hazards_locations_circle)): ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.hazards_locations_circle[i], env.hazards_radius, color='r')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[0][0], env.hazards_locations_line[0][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[1][0], env.hazards_locations_line[1][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[2][0], env.hazards_locations_line[2][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[3][0], env.hazards_locations_line[3][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) car_width = 0.4 car_height = 0.3 pose = env.get_pose() car = plt.Rectangle(([pose[0] - 0.2, pose[1] - 0.15]), 0.4, 0.3, angle=np.rad2deg(pose[4])) ax.add_patch(car) p_theta = plt.quiver(pose[0], pose[1], pose[0] + .3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) # 箭头 plt.xlim([-3.0, 3.0]) plt.ylim([-3.0, 3.0]) ax.set_aspect('equal', 'box') x_positions = [] y_positions = [] start_time = time.time() while True: car_center = (pose[0], pose[1]) rect_x = car_center[0] - (car_width / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) + (car_height / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) rect_y = car_center[1] - (car_height / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) - (car_width / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) # 设置矩形的新位置和角度 car.set_xy((rect_x, rect_y)) x_positions.append(pose[0]) y_positions.append(pose[1]) car.angle = np.rad2deg(pose[4]) p_theta.XY[:, 0] = pose[0] p_theta.XY[:, 1] = pose[1] p_theta.set_UVC(.3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) step_time_start = time.time() action = agent.predict(obs) single_step_time = time.time() - step_time_start next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) pose = env.get_pose() total_reward += reward obs = next_obs plt.plot(x_positions, y_positions) if done: delta_time = time.time() - start_time break plt.title('QLearning算法轨迹图') plt.savefig('Q_traj.png', dpi=300) return env.dist_2_goal, env.travel_dist, env.episode_step, delta_time, single_step_time from matplotlib import animation def Qdisplay_frames_as_gif(frames, file_name): patch = plt.imshow(frames[0]) plt.axis('off') def animate(i): patch.set_data(frames[i]) anim = animation.FuncAnimation(plt.gcf(), animate, frames=len(frames), interval=5) anim.save(file_name, writer='pillow', fps=30)
def run_episode(env, agent, episode, render=False): total_steps = 0 # 记录每个episode走了多少step total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() # 重置环境, 重新开一局(即开始新的一个episode) while True: action = agent.sample(obs, episode) # 根据算法选择一个动作 next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) # 与环境进行一个交互 # 训练 Q-learning算法 agent.learn(obs, action, reward, next_obs, done) obs = next_obs # 存储上一个观察值 total_reward += reward total_steps += 1 # 计算step数 if render: env.render() # 渲染新的一帧图形 if done: break return total_reward, total_steps def test_Q_episode(env, agent, draw=False, render=False): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() trajectory_list = [] Qframes = [] while True: action = agent.predict(obs) # greedy next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) total_reward += reward obs = next_obs if render: Qframes.append(env.render(mode='rgb_array')) if done: break trajectory_list.append(np.array([next_obs / 70, next_obs % 70])) trajectory_array = np.array(trajectory_list) if draw: plt.plot(trajectory_array[:, 0], trajectory_array[:, 1]) plt.show() # Qdisplay_frames_as_gif(Qframes, 'qlearning.gif') return total_reward, trajectory_array def show_Q_traj(env, agent): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() fig, ax = plt.subplots() for i in range(len(env.hazards_locations_circle)): ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.hazards_locations_circle[i], env.hazards_radius, color='r')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[0][0], env.hazards_locations_line[0][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[1][0], env.hazards_locations_line[1][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[2][0], env.hazards_locations_line[2][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[3][0], env.hazards_locations_line[3][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) car_width = 0.4 car_height = 0.3 pose = env.get_pose() car = plt.Rectangle(([pose[0] - 0.2, pose[1] - 0.15]), 0.4, 0.3, angle=np.rad2deg(pose[4])) ax.add_patch(car) p_theta = plt.quiver(pose[0], pose[1], pose[0] + .3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) # 箭头 plt.xlim([-3.0, 3.0]) plt.ylim([-3.0, 3.0]) ax.set_aspect('equal', 'box') x_positions = [] y_positions = [] start_time = time.time() while True: car_center = (pose[0], pose[1]) rect_x = car_center[0] - (car_width / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) + (car_height / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) rect_y = car_center[1] - (car_height / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) - (car_width / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) # 设置矩形的新位置和角度 car.set_xy((rect_x, rect_y)) x_positions.append(pose[0]) y_positions.append(pose[1]) car.angle = np.rad2deg(pose[4]) p_theta.XY[:, 0] = pose[0] p_theta.XY[:, 1] = pose[1] p_theta.set_UVC(.3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) step_time_start = time.time() action = agent.predict(obs) single_step_time = time.time() - step_time_start next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) pose = env.get_pose() total_reward += reward obs = next_obs plt.plot(x_positions, y_positions) if done: delta_time = time.time() - start_time break plt.title('QLearning算法轨迹图') plt.savefig('Q_traj.png', dpi=300) return env.dist_2_goal, env.travel_dist, env.episode_step, delta_time, single_step_time from matplotlib import animation def Qdisplay_frames_as_gif(frames, file_name): patch = plt.imshow(frames[0]) plt.axis('off') def animate(i): patch.set_data(frames[i]) anim = animation.FuncAnimation(plt.gcf(), animate, frames=len(frames), interval=5) anim.save(file_name, writer='pillow', fps=30)
env = UnicycleEnv() # 初始化环境
# 创建一个agent实例,输入超参数
agent = QLearningAgent(
obs_n=70 * 70,
act_n=3,
learning_rate=0.2,
gamma=0.99,
epsilon_coefficient=0.5)
log_f = open("log_QLearning.txt", "w+", encoding='utf-8')
for episode in range(3000):
ep_reward, ep_steps = run_episode(env, agent, episode, False)
print('Episode %s: steps = %s , reward = %.4f' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward))
log_f.write('E:%d, S:%d, R:%.4f\n' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward))
log_f.flush()
agent.save()
# 全部训练结束,查看算法效果
test_reward, _ = test_Q_episode(env, agent, render=False)
print('test reward = %.4f' % (test_reward))
env = UnicycleEnv() # 初始化环境 # 创建一个agent实例,输入超参数 agent = QLearningAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.5) log_f = open("log_QLearning.txt", "w+", encoding='utf-8') for episode in range(3000): ep_reward, ep_steps = run_episode(env, agent, episode, False) print('Episode %s: steps = %s , reward = %.4f' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.write('E:%d, S:%d, R:%.4f\n' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.flush() agent.save() # 全部训练结束,查看算法效果 test_reward, _ = test_Q_episode(env, agent, render=False) print('test reward = %.4f' % (test_reward))
复制env = UnicycleEnv() # 初始化环境 # 创建一个agent实例,输入超参数 agent = QLearningAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.5) log_f = open("log_QLearning.txt", "w+", encoding='utf-8') for episode in range(3000): ep_reward, ep_steps = run_episode(env, agent, episode, False) print('Episode %s: steps = %s , reward = %.4f' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.write('E:%d, S:%d, R:%.4f\n' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.flush() agent.save() # 全部训练结束,查看算法效果 test_reward, _ = test_Q_episode(env, agent, render=False) print('test reward = %.4f' % (test_reward))
env = UnicycleEnv() # 初始化环境 # 创建一个agent实例,输入超参数 agent = QLearningAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.5) log_f = open("log_QLearning.txt", "w+", encoding='utf-8') for episode in range(3000): ep_reward, ep_steps = run_episode(env, agent, episode, False) print('Episode %s: steps = %s , reward = %.4f' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.write('E:%d, S:%d, R:%.4f\n' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.flush() agent.save() # 全部训练结束,查看算法效果 test_reward, _ = test_Q_episode(env, agent, render=False) print('test reward = %.4f' % (test_reward))
env = UnicycleEnv() # 初始化环境 # 创建一个agent实例,输入超参数 agent = QLearningAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.5) log_f = open("log_QLearning.txt", "w+", encoding='utf-8') for episode in range(3000): ep_reward, ep_steps = run_episode(env, agent, episode, False) print('Episode %s: steps = %s , reward = %.4f' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.write('E:%d, S:%d, R:%.4f\n' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.flush() agent.save() # 全部训练结束,查看算法效果 test_reward, _ = test_Q_episode(env, agent, render=False) print('test reward = %.4f' % (test_reward))
Episode 2989: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819
Episode 2990: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819
Episode 2991: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819
Episode 2992: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819
Episode 2993: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819
Episode 2994: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819
Episode 2995: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819
Episode 2996: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819
Episode 2997: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819
Episode 2998: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819
......
test reward = 4.7819
Episode 2989: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2990: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2991: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2992: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2993: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2994: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2995: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2996: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2997: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2998: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 ...... test reward = 4.7819
复制 Episode 2989: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2990: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2991: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2992: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2993: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2994: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2995: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2996: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2997: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2998: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 ...... test reward = 4.7819
Episode 2989: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2990: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2991: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2992: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2993: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2994: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2995: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2996: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2997: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 Episode 2998: steps = 201 , reward = 4.7819 ...... test reward = 4.7819
def run_episode(env, agent, episode, render=False):
total_steps = 0 # 记录每个episode走了多少step
total_reward = 0
obs = env.reset() # 重置环境, 重新开一局(即开始新的一个episode)
action = agent.sample(obs, episode) # 根据算法选择一个动作
while True:
next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) # 与环境进行一个交互
next_action = agent.sample(next_obs, episode) # 根据算法选择一个动作
# 训练 Sarsa 算法
agent.learn(obs, action, reward, next_obs, next_action, done)
action = next_action
obs = next_obs # 存储上一个观察值
total_reward += reward
total_steps += 1 # 计算step数
if render:
env.render() # 渲染新的一帧图形
if done:
break
return total_reward, total_steps
def test_S_episode(env, agent, draw=False, render=False):
total_reward = 0
obs = env.reset()
trajectory_list = []
Sframes = []
while True:
action = agent.predict(obs) # greedy
next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
total_reward += reward
obs = next_obs
if render:
Sframes.append(env.render(mode='rgb_array'))
if done:
break
trajectory_list.append(np.array([next_obs / 70, next_obs % 70]))
trajectory_array = np.array(trajectory_list)
if draw:
plt.plot(trajectory_array[:, 0], trajectory_array[:, 1])
plt.show()
# Sdisplay_frames_as_gif(Sframes, 'sarsa.gif')
return total_reward, trajectory_array
def show_S_traj(env, agent):
total_reward = 0
obs = env.reset()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
for i in range(len(env.hazards_locations_circle)):
ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.hazards_locations_circle[i], env.hazards_radius, color='r'))
ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g'))
ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g'))
line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[0][0], env.hazards_locations_line[0][1]),
(env.hazards_locations_line[1][0], env.hazards_locations_line[1][1]), "data", "data",
color='r', linewidth=5)
ax.add_patch(line)
line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[2][0], env.hazards_locations_line[2][1]),
(env.hazards_locations_line[3][0], env.hazards_locations_line[3][1]), "data", "data",
color='r', linewidth=5)
ax.add_patch(line)
car_width = 0.4
car_height = 0.3
pose = env.get_pose()
car = plt.Rectangle(([pose[0] - 0.2, pose[1] - 0.15]), 0.4, 0.3, angle=np.rad2deg(pose[4]))
ax.add_patch(car)
p_theta = plt.quiver(pose[0], pose[1], pose[0] + .3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) # 箭头
plt.xlim([-3.0, 3.0])
plt.ylim([-3.0, 3.0])
ax.set_aspect('equal', 'box')
x_positions = []
y_positions = []
start_time = time.time()
while True:
car_center = (pose[0], pose[1])
rect_x = car_center[0] - (car_width / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) + (car_height / 2) * np.sin(pose[4])
rect_y = car_center[1] - (car_height / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) - (car_width / 2) * np.sin(pose[4])
# 设置矩形的新位置和角度
car.set_xy((rect_x, rect_y))
x_positions.append(pose[0])
y_positions.append(pose[1])
car.angle = np.rad2deg(pose[4])
p_theta.XY[:, 0] = pose[0]
p_theta.XY[:, 1] = pose[1]
p_theta.set_UVC(.3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3])
step_time_start = time.time()
action = agent.predict(obs)
single_step_time = time.time() - step_time_start
next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
pose = env.get_pose()
total_reward += reward
obs = next_obs
plt.plot(x_positions, y_positions)
if done:
delta_time = time.time() - start_time
break
plt.title('Sarsa算法轨迹图')
plt.savefig('S_traj.png', dpi=300)
return env.dist_2_goal, env.travel_dist, env.episode_step, delta_time, single_step_time
from matplotlib import animation
def Sdisplay_frames_as_gif(frames, file_name):
patch = plt.imshow(frames[0])
plt.axis('off')
def animate(i):
patch.set_data(frames[i])
anim = animation.FuncAnimation(plt.gcf(), animate, frames=len(frames), interval=5)
anim.save(file_name, writer='pillow', fps=30)
def run_episode(env, agent, episode, render=False): total_steps = 0 # 记录每个episode走了多少step total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() # 重置环境, 重新开一局(即开始新的一个episode) action = agent.sample(obs, episode) # 根据算法选择一个动作 while True: next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) # 与环境进行一个交互 next_action = agent.sample(next_obs, episode) # 根据算法选择一个动作 # 训练 Sarsa 算法 agent.learn(obs, action, reward, next_obs, next_action, done) action = next_action obs = next_obs # 存储上一个观察值 total_reward += reward total_steps += 1 # 计算step数 if render: env.render() # 渲染新的一帧图形 if done: break return total_reward, total_steps def test_S_episode(env, agent, draw=False, render=False): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() trajectory_list = [] Sframes = [] while True: action = agent.predict(obs) # greedy next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) total_reward += reward obs = next_obs if render: Sframes.append(env.render(mode='rgb_array')) if done: break trajectory_list.append(np.array([next_obs / 70, next_obs % 70])) trajectory_array = np.array(trajectory_list) if draw: plt.plot(trajectory_array[:, 0], trajectory_array[:, 1]) plt.show() # Sdisplay_frames_as_gif(Sframes, 'sarsa.gif') return total_reward, trajectory_array def show_S_traj(env, agent): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() fig, ax = plt.subplots() for i in range(len(env.hazards_locations_circle)): ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.hazards_locations_circle[i], env.hazards_radius, color='r')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[0][0], env.hazards_locations_line[0][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[1][0], env.hazards_locations_line[1][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[2][0], env.hazards_locations_line[2][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[3][0], env.hazards_locations_line[3][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) car_width = 0.4 car_height = 0.3 pose = env.get_pose() car = plt.Rectangle(([pose[0] - 0.2, pose[1] - 0.15]), 0.4, 0.3, angle=np.rad2deg(pose[4])) ax.add_patch(car) p_theta = plt.quiver(pose[0], pose[1], pose[0] + .3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) # 箭头 plt.xlim([-3.0, 3.0]) plt.ylim([-3.0, 3.0]) ax.set_aspect('equal', 'box') x_positions = [] y_positions = [] start_time = time.time() while True: car_center = (pose[0], pose[1]) rect_x = car_center[0] - (car_width / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) + (car_height / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) rect_y = car_center[1] - (car_height / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) - (car_width / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) # 设置矩形的新位置和角度 car.set_xy((rect_x, rect_y)) x_positions.append(pose[0]) y_positions.append(pose[1]) car.angle = np.rad2deg(pose[4]) p_theta.XY[:, 0] = pose[0] p_theta.XY[:, 1] = pose[1] p_theta.set_UVC(.3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) step_time_start = time.time() action = agent.predict(obs) single_step_time = time.time() - step_time_start next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) pose = env.get_pose() total_reward += reward obs = next_obs plt.plot(x_positions, y_positions) if done: delta_time = time.time() - start_time break plt.title('Sarsa算法轨迹图') plt.savefig('S_traj.png', dpi=300) return env.dist_2_goal, env.travel_dist, env.episode_step, delta_time, single_step_time from matplotlib import animation def Sdisplay_frames_as_gif(frames, file_name): patch = plt.imshow(frames[0]) plt.axis('off') def animate(i): patch.set_data(frames[i]) anim = animation.FuncAnimation(plt.gcf(), animate, frames=len(frames), interval=5) anim.save(file_name, writer='pillow', fps=30)
复制def run_episode(env, agent, episode, render=False): total_steps = 0 # 记录每个episode走了多少step total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() # 重置环境, 重新开一局(即开始新的一个episode) action = agent.sample(obs, episode) # 根据算法选择一个动作 while True: next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) # 与环境进行一个交互 next_action = agent.sample(next_obs, episode) # 根据算法选择一个动作 # 训练 Sarsa 算法 agent.learn(obs, action, reward, next_obs, next_action, done) action = next_action obs = next_obs # 存储上一个观察值 total_reward += reward total_steps += 1 # 计算step数 if render: env.render() # 渲染新的一帧图形 if done: break return total_reward, total_steps def test_S_episode(env, agent, draw=False, render=False): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() trajectory_list = [] Sframes = [] while True: action = agent.predict(obs) # greedy next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) total_reward += reward obs = next_obs if render: Sframes.append(env.render(mode='rgb_array')) if done: break trajectory_list.append(np.array([next_obs / 70, next_obs % 70])) trajectory_array = np.array(trajectory_list) if draw: plt.plot(trajectory_array[:, 0], trajectory_array[:, 1]) plt.show() # Sdisplay_frames_as_gif(Sframes, 'sarsa.gif') return total_reward, trajectory_array def show_S_traj(env, agent): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() fig, ax = plt.subplots() for i in range(len(env.hazards_locations_circle)): ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.hazards_locations_circle[i], env.hazards_radius, color='r')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[0][0], env.hazards_locations_line[0][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[1][0], env.hazards_locations_line[1][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[2][0], env.hazards_locations_line[2][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[3][0], env.hazards_locations_line[3][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) car_width = 0.4 car_height = 0.3 pose = env.get_pose() car = plt.Rectangle(([pose[0] - 0.2, pose[1] - 0.15]), 0.4, 0.3, angle=np.rad2deg(pose[4])) ax.add_patch(car) p_theta = plt.quiver(pose[0], pose[1], pose[0] + .3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) # 箭头 plt.xlim([-3.0, 3.0]) plt.ylim([-3.0, 3.0]) ax.set_aspect('equal', 'box') x_positions = [] y_positions = [] start_time = time.time() while True: car_center = (pose[0], pose[1]) rect_x = car_center[0] - (car_width / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) + (car_height / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) rect_y = car_center[1] - (car_height / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) - (car_width / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) # 设置矩形的新位置和角度 car.set_xy((rect_x, rect_y)) x_positions.append(pose[0]) y_positions.append(pose[1]) car.angle = np.rad2deg(pose[4]) p_theta.XY[:, 0] = pose[0] p_theta.XY[:, 1] = pose[1] p_theta.set_UVC(.3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) step_time_start = time.time() action = agent.predict(obs) single_step_time = time.time() - step_time_start next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) pose = env.get_pose() total_reward += reward obs = next_obs plt.plot(x_positions, y_positions) if done: delta_time = time.time() - start_time break plt.title('Sarsa算法轨迹图') plt.savefig('S_traj.png', dpi=300) return env.dist_2_goal, env.travel_dist, env.episode_step, delta_time, single_step_time from matplotlib import animation def Sdisplay_frames_as_gif(frames, file_name): patch = plt.imshow(frames[0]) plt.axis('off') def animate(i): patch.set_data(frames[i]) anim = animation.FuncAnimation(plt.gcf(), animate, frames=len(frames), interval=5) anim.save(file_name, writer='pillow', fps=30)
def run_episode(env, agent, episode, render=False): total_steps = 0 # 记录每个episode走了多少step total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() # 重置环境, 重新开一局(即开始新的一个episode) action = agent.sample(obs, episode) # 根据算法选择一个动作 while True: next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) # 与环境进行一个交互 next_action = agent.sample(next_obs, episode) # 根据算法选择一个动作 # 训练 Sarsa 算法 agent.learn(obs, action, reward, next_obs, next_action, done) action = next_action obs = next_obs # 存储上一个观察值 total_reward += reward total_steps += 1 # 计算step数 if render: env.render() # 渲染新的一帧图形 if done: break return total_reward, total_steps def test_S_episode(env, agent, draw=False, render=False): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() trajectory_list = [] Sframes = [] while True: action = agent.predict(obs) # greedy next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) total_reward += reward obs = next_obs if render: Sframes.append(env.render(mode='rgb_array')) if done: break trajectory_list.append(np.array([next_obs / 70, next_obs % 70])) trajectory_array = np.array(trajectory_list) if draw: plt.plot(trajectory_array[:, 0], trajectory_array[:, 1]) plt.show() # Sdisplay_frames_as_gif(Sframes, 'sarsa.gif') return total_reward, trajectory_array def show_S_traj(env, agent): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() fig, ax = plt.subplots() for i in range(len(env.hazards_locations_circle)): ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.hazards_locations_circle[i], env.hazards_radius, color='r')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[0][0], env.hazards_locations_line[0][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[1][0], env.hazards_locations_line[1][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[2][0], env.hazards_locations_line[2][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[3][0], env.hazards_locations_line[3][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) car_width = 0.4 car_height = 0.3 pose = env.get_pose() car = plt.Rectangle(([pose[0] - 0.2, pose[1] - 0.15]), 0.4, 0.3, angle=np.rad2deg(pose[4])) ax.add_patch(car) p_theta = plt.quiver(pose[0], pose[1], pose[0] + .3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) # 箭头 plt.xlim([-3.0, 3.0]) plt.ylim([-3.0, 3.0]) ax.set_aspect('equal', 'box') x_positions = [] y_positions = [] start_time = time.time() while True: car_center = (pose[0], pose[1]) rect_x = car_center[0] - (car_width / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) + (car_height / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) rect_y = car_center[1] - (car_height / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) - (car_width / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) # 设置矩形的新位置和角度 car.set_xy((rect_x, rect_y)) x_positions.append(pose[0]) y_positions.append(pose[1]) car.angle = np.rad2deg(pose[4]) p_theta.XY[:, 0] = pose[0] p_theta.XY[:, 1] = pose[1] p_theta.set_UVC(.3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) step_time_start = time.time() action = agent.predict(obs) single_step_time = time.time() - step_time_start next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) pose = env.get_pose() total_reward += reward obs = next_obs plt.plot(x_positions, y_positions) if done: delta_time = time.time() - start_time break plt.title('Sarsa算法轨迹图') plt.savefig('S_traj.png', dpi=300) return env.dist_2_goal, env.travel_dist, env.episode_step, delta_time, single_step_time from matplotlib import animation def Sdisplay_frames_as_gif(frames, file_name): patch = plt.imshow(frames[0]) plt.axis('off') def animate(i): patch.set_data(frames[i]) anim = animation.FuncAnimation(plt.gcf(), animate, frames=len(frames), interval=5) anim.save(file_name, writer='pillow', fps=30)
def run_episode(env, agent, episode, render=False): total_steps = 0 # 记录每个episode走了多少step total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() # 重置环境, 重新开一局(即开始新的一个episode) action = agent.sample(obs, episode) # 根据算法选择一个动作 while True: next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) # 与环境进行一个交互 next_action = agent.sample(next_obs, episode) # 根据算法选择一个动作 # 训练 Sarsa 算法 agent.learn(obs, action, reward, next_obs, next_action, done) action = next_action obs = next_obs # 存储上一个观察值 total_reward += reward total_steps += 1 # 计算step数 if render: env.render() # 渲染新的一帧图形 if done: break return total_reward, total_steps def test_S_episode(env, agent, draw=False, render=False): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() trajectory_list = [] Sframes = [] while True: action = agent.predict(obs) # greedy next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) total_reward += reward obs = next_obs if render: Sframes.append(env.render(mode='rgb_array')) if done: break trajectory_list.append(np.array([next_obs / 70, next_obs % 70])) trajectory_array = np.array(trajectory_list) if draw: plt.plot(trajectory_array[:, 0], trajectory_array[:, 1]) plt.show() # Sdisplay_frames_as_gif(Sframes, 'sarsa.gif') return total_reward, trajectory_array def show_S_traj(env, agent): total_reward = 0 obs = env.reset() fig, ax = plt.subplots() for i in range(len(env.hazards_locations_circle)): ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.hazards_locations_circle[i], env.hazards_radius, color='r')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(env.goal_pos, env.goal_size, color='g')) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[0][0], env.hazards_locations_line[0][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[1][0], env.hazards_locations_line[1][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) line = patches.ConnectionPatch((env.hazards_locations_line[2][0], env.hazards_locations_line[2][1]), (env.hazards_locations_line[3][0], env.hazards_locations_line[3][1]), "data", "data", color='r', linewidth=5) ax.add_patch(line) car_width = 0.4 car_height = 0.3 pose = env.get_pose() car = plt.Rectangle(([pose[0] - 0.2, pose[1] - 0.15]), 0.4, 0.3, angle=np.rad2deg(pose[4])) ax.add_patch(car) p_theta = plt.quiver(pose[0], pose[1], pose[0] + .3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) # 箭头 plt.xlim([-3.0, 3.0]) plt.ylim([-3.0, 3.0]) ax.set_aspect('equal', 'box') x_positions = [] y_positions = [] start_time = time.time() while True: car_center = (pose[0], pose[1]) rect_x = car_center[0] - (car_width / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) + (car_height / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) rect_y = car_center[1] - (car_height / 2) * np.cos(pose[4]) - (car_width / 2) * np.sin(pose[4]) # 设置矩形的新位置和角度 car.set_xy((rect_x, rect_y)) x_positions.append(pose[0]) y_positions.append(pose[1]) car.angle = np.rad2deg(pose[4]) p_theta.XY[:, 0] = pose[0] p_theta.XY[:, 1] = pose[1] p_theta.set_UVC(.3 * pose[2], .3 * pose[3]) step_time_start = time.time() action = agent.predict(obs) single_step_time = time.time() - step_time_start next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) pose = env.get_pose() total_reward += reward obs = next_obs plt.plot(x_positions, y_positions) if done: delta_time = time.time() - start_time break plt.title('Sarsa算法轨迹图') plt.savefig('S_traj.png', dpi=300) return env.dist_2_goal, env.travel_dist, env.episode_step, delta_time, single_step_time from matplotlib import animation def Sdisplay_frames_as_gif(frames, file_name): patch = plt.imshow(frames[0]) plt.axis('off') def animate(i): patch.set_data(frames[i]) anim = animation.FuncAnimation(plt.gcf(), animate, frames=len(frames), interval=5) anim.save(file_name, writer='pillow', fps=30)
env = UnicycleEnv() # 初始化环境
# 创建一个agent实例,输入超参数
agent = SarsaAgent(
obs_n=70 * 70,
act_n=3,
learning_rate=0.2,
gamma=0.99,
epsilon_coefficient=0.6)
# 日志文件
log_f = open("log_Sarsa.txt", "w+", encoding='utf-8')
# 训练3000个episode,打印每个episode的分数
for episode in range(3000):
ep_reward, ep_steps = run_episode(env, agent, episode, False)
print('Episode %s: steps = %s , reward = %.4f' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward))
log_f.write('E:%d, S:%d, R:%.4f\n' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward))
log_f.flush()
agent.save()
# 全部训练结束,查看算法效果
test_reward, _ = test_S_episode(env, agent, render=False)
print('test reward = %.4f' % (test_reward))
env = UnicycleEnv() # 初始化环境 # 创建一个agent实例,输入超参数 agent = SarsaAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.6) # 日志文件 log_f = open("log_Sarsa.txt", "w+", encoding='utf-8') # 训练3000个episode,打印每个episode的分数 for episode in range(3000): ep_reward, ep_steps = run_episode(env, agent, episode, False) print('Episode %s: steps = %s , reward = %.4f' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.write('E:%d, S:%d, R:%.4f\n' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.flush() agent.save() # 全部训练结束,查看算法效果 test_reward, _ = test_S_episode(env, agent, render=False) print('test reward = %.4f' % (test_reward))
复制env = UnicycleEnv() # 初始化环境 # 创建一个agent实例,输入超参数 agent = SarsaAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.6) # 日志文件 log_f = open("log_Sarsa.txt", "w+", encoding='utf-8') # 训练3000个episode,打印每个episode的分数 for episode in range(3000): ep_reward, ep_steps = run_episode(env, agent, episode, False) print('Episode %s: steps = %s , reward = %.4f' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.write('E:%d, S:%d, R:%.4f\n' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.flush() agent.save() # 全部训练结束,查看算法效果 test_reward, _ = test_S_episode(env, agent, render=False) print('test reward = %.4f' % (test_reward))
env = UnicycleEnv() # 初始化环境 # 创建一个agent实例,输入超参数 agent = SarsaAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.6) # 日志文件 log_f = open("log_Sarsa.txt", "w+", encoding='utf-8') # 训练3000个episode,打印每个episode的分数 for episode in range(3000): ep_reward, ep_steps = run_episode(env, agent, episode, False) print('Episode %s: steps = %s , reward = %.4f' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.write('E:%d, S:%d, R:%.4f\n' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.flush() agent.save() # 全部训练结束,查看算法效果 test_reward, _ = test_S_episode(env, agent, render=False) print('test reward = %.4f' % (test_reward))
env = UnicycleEnv() # 初始化环境 # 创建一个agent实例,输入超参数 agent = SarsaAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.6) # 日志文件 log_f = open("log_Sarsa.txt", "w+", encoding='utf-8') # 训练3000个episode,打印每个episode的分数 for episode in range(3000): ep_reward, ep_steps = run_episode(env, agent, episode, False) print('Episode %s: steps = %s , reward = %.4f' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.write('E:%d, S:%d, R:%.4f\n' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward)) log_f.flush() agent.save() # 全部训练结束,查看算法效果 test_reward, _ = test_S_episode(env, agent, render=False) print('test reward = %.4f' % (test_reward))
Episode 2996: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774
Episode 2997: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774
Episode 2998: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774
Episode 2999: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774
......
test reward = 4.5774
Episode 2996: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774 Episode 2997: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774 Episode 2998: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774 Episode 2999: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774 ...... test reward = 4.5774
复制 Episode 2996: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774 Episode 2997: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774 Episode 2998: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774 Episode 2999: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774 ...... test reward = 4.5774
Episode 2996: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774 Episode 2997: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774 Episode 2998: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774 Episode 2999: steps = 212 , reward = 4.5774 ...... test reward = 4.5774
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.font_manager as font_manager
# 设置显示中文
matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['FZSongYi-Z13S'] # 指定默认字体
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决保存图像是负号'-'显示为方块的问题
%matplotlib inline import matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.font_manager as font_manager # 设置显示中文 matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['FZSongYi-Z13S'] # 指定默认字体 matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决保存图像是负号'-'显示为方块的问题
复制%matplotlib inline import matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.font_manager as font_manager # 设置显示中文 matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['FZSongYi-Z13S'] # 指定默认字体 matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决保存图像是负号'-'显示为方块的问题
%matplotlib inline import matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.font_manager as font_manager # 设置显示中文 matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['FZSongYi-Z13S'] # 指定默认字体 matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决保存图像是负号'-'显示为方块的问题
%matplotlib inline import matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.font_manager as font_manager # 设置显示中文 matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['FZSongYi-Z13S'] # 指定默认字体 matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决保存图像是负号'-'显示为方块的问题
import numpy as np
from pylab import xticks, yticks
import pandas as pd
env = UnicycleEnv() # 初始化环境
# 创建一个agent实例,输入超参数
agent_Q = QLearningAgent(
obs_n=70 * 70,
act_n=3,
learning_rate=0.2,
gamma=0.99,
epsilon_coefficient=0.6)
agent_S = SarsaAgent(
obs_n=70 * 70,
act_n=3,
learning_rate=0.2,
gamma=0.99,
epsilon_coefficient=0.6)
agent_S.restore()
agent_Q.restore()
test_reward_S, trajectory_S = test_S_episode(env, agent_S, render=False)
test_reward_Q, trajectory_Q = test_Q_episode(env, agent_Q, render=False)
S_dist2goal, S_travel_dist, S_travel_steps, S_travel_time, S_single_step_time = show_S_traj(env, agent_S)
Q_dist2goal, Q_travel_dist, Q_travel_steps, Q_travel_time, Q_single_step_time = show_Q_traj(env, agent_Q)
data = {"算法": ["QLearning", "Sarsa"],
"直线距离(m)": [Q_dist2goal, S_dist2goal],
"轨迹距离(m)": [Q_travel_dist, S_travel_dist],
"运行步数": [Q_travel_steps, S_travel_steps],
"总时间(ms)": [Q_travel_time * 1000, S_travel_time * 1000],
"单步时间(ms)": [Q_travel_time / Q_travel_steps * 1000, S_travel_time / S_travel_steps * 1000],
"碰撞": [0, 0]}
pd.DataFrame(data)
import numpy as np from pylab import xticks, yticks import pandas as pd env = UnicycleEnv() # 初始化环境 # 创建一个agent实例,输入超参数 agent_Q = QLearningAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.6) agent_S = SarsaAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.6) agent_S.restore() agent_Q.restore() test_reward_S, trajectory_S = test_S_episode(env, agent_S, render=False) test_reward_Q, trajectory_Q = test_Q_episode(env, agent_Q, render=False) S_dist2goal, S_travel_dist, S_travel_steps, S_travel_time, S_single_step_time = show_S_traj(env, agent_S) Q_dist2goal, Q_travel_dist, Q_travel_steps, Q_travel_time, Q_single_step_time = show_Q_traj(env, agent_Q) data = {"算法": ["QLearning", "Sarsa"], "直线距离(m)": [Q_dist2goal, S_dist2goal], "轨迹距离(m)": [Q_travel_dist, S_travel_dist], "运行步数": [Q_travel_steps, S_travel_steps], "总时间(ms)": [Q_travel_time * 1000, S_travel_time * 1000], "单步时间(ms)": [Q_travel_time / Q_travel_steps * 1000, S_travel_time / S_travel_steps * 1000], "碰撞": [0, 0]} pd.DataFrame(data)
复制import numpy as np from pylab import xticks, yticks import pandas as pd env = UnicycleEnv() # 初始化环境 # 创建一个agent实例,输入超参数 agent_Q = QLearningAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.6) agent_S = SarsaAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.6) agent_S.restore() agent_Q.restore() test_reward_S, trajectory_S = test_S_episode(env, agent_S, render=False) test_reward_Q, trajectory_Q = test_Q_episode(env, agent_Q, render=False) S_dist2goal, S_travel_dist, S_travel_steps, S_travel_time, S_single_step_time = show_S_traj(env, agent_S) Q_dist2goal, Q_travel_dist, Q_travel_steps, Q_travel_time, Q_single_step_time = show_Q_traj(env, agent_Q) data = {"算法": ["QLearning", "Sarsa"], "直线距离(m)": [Q_dist2goal, S_dist2goal], "轨迹距离(m)": [Q_travel_dist, S_travel_dist], "运行步数": [Q_travel_steps, S_travel_steps], "总时间(ms)": [Q_travel_time * 1000, S_travel_time * 1000], "单步时间(ms)": [Q_travel_time / Q_travel_steps * 1000, S_travel_time / S_travel_steps * 1000], "碰撞": [0, 0]} pd.DataFrame(data)
import numpy as np from pylab import xticks, yticks import pandas as pd env = UnicycleEnv() # 初始化环境 # 创建一个agent实例,输入超参数 agent_Q = QLearningAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.6) agent_S = SarsaAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.6) agent_S.restore() agent_Q.restore() test_reward_S, trajectory_S = test_S_episode(env, agent_S, render=False) test_reward_Q, trajectory_Q = test_Q_episode(env, agent_Q, render=False) S_dist2goal, S_travel_dist, S_travel_steps, S_travel_time, S_single_step_time = show_S_traj(env, agent_S) Q_dist2goal, Q_travel_dist, Q_travel_steps, Q_travel_time, Q_single_step_time = show_Q_traj(env, agent_Q) data = {"算法": ["QLearning", "Sarsa"], "直线距离(m)": [Q_dist2goal, S_dist2goal], "轨迹距离(m)": [Q_travel_dist, S_travel_dist], "运行步数": [Q_travel_steps, S_travel_steps], "总时间(ms)": [Q_travel_time * 1000, S_travel_time * 1000], "单步时间(ms)": [Q_travel_time / Q_travel_steps * 1000, S_travel_time / S_travel_steps * 1000], "碰撞": [0, 0]} pd.DataFrame(data)
import numpy as np from pylab import xticks, yticks import pandas as pd env = UnicycleEnv() # 初始化环境 # 创建一个agent实例,输入超参数 agent_Q = QLearningAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.6) agent_S = SarsaAgent( obs_n=70 * 70, act_n=3, learning_rate=0.2, gamma=0.99, epsilon_coefficient=0.6) agent_S.restore() agent_Q.restore() test_reward_S, trajectory_S = test_S_episode(env, agent_S, render=False) test_reward_Q, trajectory_Q = test_Q_episode(env, agent_Q, render=False) S_dist2goal, S_travel_dist, S_travel_steps, S_travel_time, S_single_step_time = show_S_traj(env, agent_S) Q_dist2goal, Q_travel_dist, Q_travel_steps, Q_travel_time, Q_single_step_time = show_Q_traj(env, agent_Q) data = {"算法": ["QLearning", "Sarsa"], "直线距离(m)": [Q_dist2goal, S_dist2goal], "轨迹距离(m)": [Q_travel_dist, S_travel_dist], "运行步数": [Q_travel_steps, S_travel_steps], "总时间(ms)": [Q_travel_time * 1000, S_travel_time * 1000], "单步时间(ms)": [Q_travel_time / Q_travel_steps * 1000, S_travel_time / S_travel_steps * 1000], "碰撞": [0, 0]} pd.DataFrame(data)
算法
直线距离(m)
轨迹距离(m)
运行步数
总时间(ms)
单步时间(ms)
碰撞
0
QLearning
7.071068
10.427709
201
287.226200
1.428986
0
1
Sarsa
7.071068
11.089841
212
319.726706
1.508145
0
#轨迹对比图
plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes()
ax.plot(trajectory_Q[:, 0], trajectory_Q[:, 1], label="QLearning")
ax.plot(trajectory_S[:, 0], trajectory_S[:, 1], label="Sarsa")
ax.legend()
xticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True))
yticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True))
ax.grid(axis='x', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5)
ax.grid(axis='y', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5)
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter())
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter())
plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法轨迹对比图')
plt.savefig('S_Q_traj.png', dpi=300)
#轨迹对比图 plt.figure() ax = plt.axes() ax.plot(trajectory_Q[:, 0], trajectory_Q[:, 1], label="QLearning") ax.plot(trajectory_S[:, 0], trajectory_S[:, 1], label="Sarsa") ax.legend() xticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) yticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) ax.grid(axis='x', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.grid(axis='y', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法轨迹对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_traj.png', dpi=300)
复制#轨迹对比图 plt.figure() ax = plt.axes() ax.plot(trajectory_Q[:, 0], trajectory_Q[:, 1], label="QLearning") ax.plot(trajectory_S[:, 0], trajectory_S[:, 1], label="Sarsa") ax.legend() xticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) yticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) ax.grid(axis='x', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.grid(axis='y', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法轨迹对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_traj.png', dpi=300)
#轨迹对比图 plt.figure() ax = plt.axes() ax.plot(trajectory_Q[:, 0], trajectory_Q[:, 1], label="QLearning") ax.plot(trajectory_S[:, 0], trajectory_S[:, 1], label="Sarsa") ax.legend() xticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) yticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) ax.grid(axis='x', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.grid(axis='y', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法轨迹对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_traj.png', dpi=300)
#轨迹对比图 plt.figure() ax = plt.axes() ax.plot(trajectory_Q[:, 0], trajectory_Q[:, 1], label="QLearning") ax.plot(trajectory_S[:, 0], trajectory_S[:, 1], label="Sarsa") ax.legend() xticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) yticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) ax.grid(axis='x', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.grid(axis='y', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法轨迹对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_traj.png', dpi=300)
with open('log_Sarsa.txt', 'r') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
S_E = []
S_S = []
S_R = []
for line in lines:
parts = line.strip().split(', ')
S_E.append(int(parts[0][2:]))
S_S.append(int(parts[1][2:]))
S_R.append(float(parts[2][2:]))
with open('log_QLearning.txt', 'r') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
Q_E = []
Q_S = []
Q_R = []
for line in lines:
parts = line.strip().split(', ')
Q_E.append(int(parts[0][2:]))
Q_S.append(int(parts[1][2:]))
Q_R.append(float(parts[2][2:]))
def moving_average(interval, windowsize):
window = np.ones(int(windowsize)) / float(windowsize)
re = np.convolve(interval, window, 'valid')
return re
wid = 5 #平滑曲线窗口宽度
Q_R_filter = moving_average(Q_R, wid)
S_R_filter = moving_average(S_R, wid)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(Q_E[:-wid + 1], Q_R_filter, label="QLearning")
plt.plot(S_E[:-wid + 1], S_R_filter, label="Sarsa")
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('训练步数')
plt.ylabel('分数')
plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法训练过程得分对比图')
plt.savefig('S_Q_reward.png', dpi=300)
Q_S_filter = moving_average(Q_S, wid)
S_S_filter = moving_average(S_S, wid)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(Q_E[:-wid + 1], Q_S_filter, label="QLearning")
plt.plot(S_E[:-wid + 1], S_S_filter, label="Sarsa")
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('训练步数')
plt.ylabel('步长')
plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法训练过程步长对比图')
plt.savefig('S_Q_steps.png', dpi=300)
.plot(trajectory_Q[:, 0], trajectory_Q[:, 1], label="QLearning")
ax.plot(trajectory_S[:, 0], trajectory_S[:, 1], label="Sarsa")
ax.legend()
xticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True))
yticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True))
ax.grid(axis='x', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5)
ax.grid(axis='y', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5)
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter())
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter())
plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法轨迹对比图')
plt.savefig('S_Q_traj.png', dpi=300)
with open('log_Sarsa.txt', 'r') as file: lines = file.readlines() S_E = [] S_S = [] S_R = [] for line in lines: parts = line.strip().split(', ') S_E.append(int(parts[0][2:])) S_S.append(int(parts[1][2:])) S_R.append(float(parts[2][2:])) with open('log_QLearning.txt', 'r') as file: lines = file.readlines() Q_E = [] Q_S = [] Q_R = [] for line in lines: parts = line.strip().split(', ') Q_E.append(int(parts[0][2:])) Q_S.append(int(parts[1][2:])) Q_R.append(float(parts[2][2:])) def moving_average(interval, windowsize): window = np.ones(int(windowsize)) / float(windowsize) re = np.convolve(interval, window, 'valid') return re wid = 5 #平滑曲线窗口宽度 Q_R_filter = moving_average(Q_R, wid) S_R_filter = moving_average(S_R, wid) plt.figure() plt.plot(Q_E[:-wid + 1], Q_R_filter, label="QLearning") plt.plot(S_E[:-wid + 1], S_R_filter, label="Sarsa") plt.legend() plt.xlabel('训练步数') plt.ylabel('分数') plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法训练过程得分对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_reward.png', dpi=300) Q_S_filter = moving_average(Q_S, wid) S_S_filter = moving_average(S_S, wid) plt.figure() plt.plot(Q_E[:-wid + 1], Q_S_filter, label="QLearning") plt.plot(S_E[:-wid + 1], S_S_filter, label="Sarsa") plt.legend() plt.xlabel('训练步数') plt.ylabel('步长') plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法训练过程步长对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_steps.png', dpi=300) .plot(trajectory_Q[:, 0], trajectory_Q[:, 1], label="QLearning") ax.plot(trajectory_S[:, 0], trajectory_S[:, 1], label="Sarsa") ax.legend() xticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) yticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) ax.grid(axis='x', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.grid(axis='y', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法轨迹对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_traj.png', dpi=300)
复制with open('log_Sarsa.txt', 'r') as file: lines = file.readlines() S_E = [] S_S = [] S_R = [] for line in lines: parts = line.strip().split(', ') S_E.append(int(parts[0][2:])) S_S.append(int(parts[1][2:])) S_R.append(float(parts[2][2:])) with open('log_QLearning.txt', 'r') as file: lines = file.readlines() Q_E = [] Q_S = [] Q_R = [] for line in lines: parts = line.strip().split(', ') Q_E.append(int(parts[0][2:])) Q_S.append(int(parts[1][2:])) Q_R.append(float(parts[2][2:])) def moving_average(interval, windowsize): window = np.ones(int(windowsize)) / float(windowsize) re = np.convolve(interval, window, 'valid') return re wid = 5 #平滑曲线窗口宽度 Q_R_filter = moving_average(Q_R, wid) S_R_filter = moving_average(S_R, wid) plt.figure() plt.plot(Q_E[:-wid + 1], Q_R_filter, label="QLearning") plt.plot(S_E[:-wid + 1], S_R_filter, label="Sarsa") plt.legend() plt.xlabel('训练步数') plt.ylabel('分数') plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法训练过程得分对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_reward.png', dpi=300) Q_S_filter = moving_average(Q_S, wid) S_S_filter = moving_average(S_S, wid) plt.figure() plt.plot(Q_E[:-wid + 1], Q_S_filter, label="QLearning") plt.plot(S_E[:-wid + 1], S_S_filter, label="Sarsa") plt.legend() plt.xlabel('训练步数') plt.ylabel('步长') plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法训练过程步长对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_steps.png', dpi=300) .plot(trajectory_Q[:, 0], trajectory_Q[:, 1], label="QLearning") ax.plot(trajectory_S[:, 0], trajectory_S[:, 1], label="Sarsa") ax.legend() xticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) yticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) ax.grid(axis='x', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.grid(axis='y', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法轨迹对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_traj.png', dpi=300)
with open('log_Sarsa.txt', 'r') as file: lines = file.readlines() S_E = [] S_S = [] S_R = [] for line in lines: parts = line.strip().split(', ') S_E.append(int(parts[0][2:])) S_S.append(int(parts[1][2:])) S_R.append(float(parts[2][2:])) with open('log_QLearning.txt', 'r') as file: lines = file.readlines() Q_E = [] Q_S = [] Q_R = [] for line in lines: parts = line.strip().split(', ') Q_E.append(int(parts[0][2:])) Q_S.append(int(parts[1][2:])) Q_R.append(float(parts[2][2:])) def moving_average(interval, windowsize): window = np.ones(int(windowsize)) / float(windowsize) re = np.convolve(interval, window, 'valid') return re wid = 5 #平滑曲线窗口宽度 Q_R_filter = moving_average(Q_R, wid) S_R_filter = moving_average(S_R, wid) plt.figure() plt.plot(Q_E[:-wid + 1], Q_R_filter, label="QLearning") plt.plot(S_E[:-wid + 1], S_R_filter, label="Sarsa") plt.legend() plt.xlabel('训练步数') plt.ylabel('分数') plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法训练过程得分对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_reward.png', dpi=300) Q_S_filter = moving_average(Q_S, wid) S_S_filter = moving_average(S_S, wid) plt.figure() plt.plot(Q_E[:-wid + 1], Q_S_filter, label="QLearning") plt.plot(S_E[:-wid + 1], S_S_filter, label="Sarsa") plt.legend() plt.xlabel('训练步数') plt.ylabel('步长') plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法训练过程步长对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_steps.png', dpi=300) .plot(trajectory_Q[:, 0], trajectory_Q[:, 1], label="QLearning") ax.plot(trajectory_S[:, 0], trajectory_S[:, 1], label="Sarsa") ax.legend() xticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) yticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) ax.grid(axis='x', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.grid(axis='y', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法轨迹对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_traj.png', dpi=300)
with open('log_Sarsa.txt', 'r') as file: lines = file.readlines() S_E = [] S_S = [] S_R = [] for line in lines: parts = line.strip().split(', ') S_E.append(int(parts[0][2:])) S_S.append(int(parts[1][2:])) S_R.append(float(parts[2][2:])) with open('log_QLearning.txt', 'r') as file: lines = file.readlines() Q_E = [] Q_S = [] Q_R = [] for line in lines: parts = line.strip().split(', ') Q_E.append(int(parts[0][2:])) Q_S.append(int(parts[1][2:])) Q_R.append(float(parts[2][2:])) def moving_average(interval, windowsize): window = np.ones(int(windowsize)) / float(windowsize) re = np.convolve(interval, window, 'valid') return re wid = 5 #平滑曲线窗口宽度 Q_R_filter = moving_average(Q_R, wid) S_R_filter = moving_average(S_R, wid) plt.figure() plt.plot(Q_E[:-wid + 1], Q_R_filter, label="QLearning") plt.plot(S_E[:-wid + 1], S_R_filter, label="Sarsa") plt.legend() plt.xlabel('训练步数') plt.ylabel('分数') plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法训练过程得分对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_reward.png', dpi=300) Q_S_filter = moving_average(Q_S, wid) S_S_filter = moving_average(S_S, wid) plt.figure() plt.plot(Q_E[:-wid + 1], Q_S_filter, label="QLearning") plt.plot(S_E[:-wid + 1], S_S_filter, label="Sarsa") plt.legend() plt.xlabel('训练步数') plt.ylabel('步长') plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法训练过程步长对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_steps.png', dpi=300) .plot(trajectory_Q[:, 0], trajectory_Q[:, 1], label="QLearning") ax.plot(trajectory_S[:, 0], trajectory_S[:, 1], label="Sarsa") ax.legend() xticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) yticks(np.linspace(0, 70, 60, endpoint=True)) ax.grid(axis='x', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.grid(axis='y', linestyle='-.', linewidth=1, color='black', alpha=0.5) ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter()) plt.title('QLearning-Sarsa算法轨迹对比图') plt.savefig('S_Q_traj.png', dpi=300)
Q_learning效果:
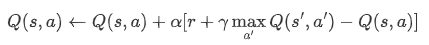

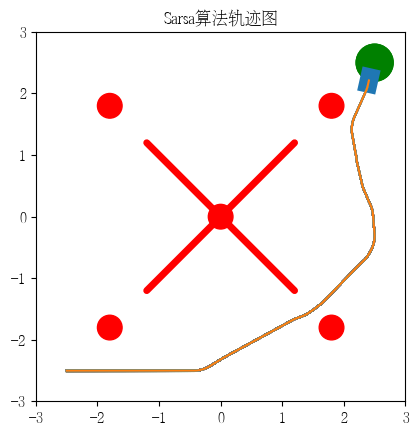
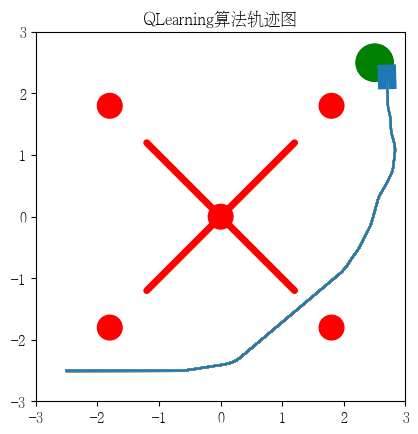
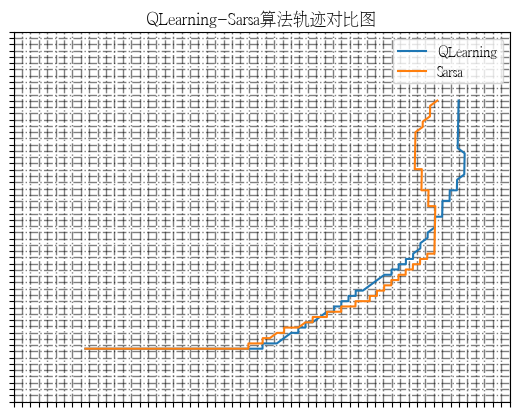
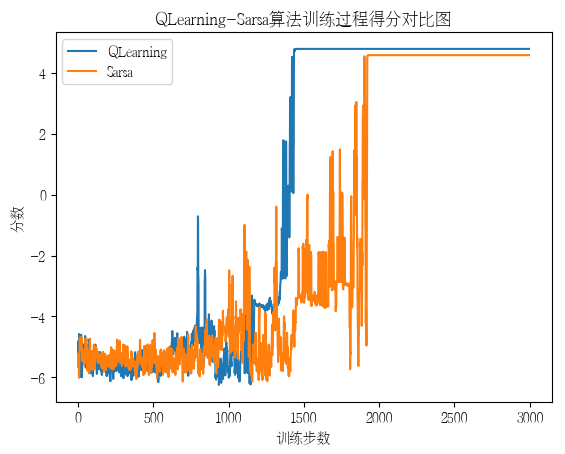
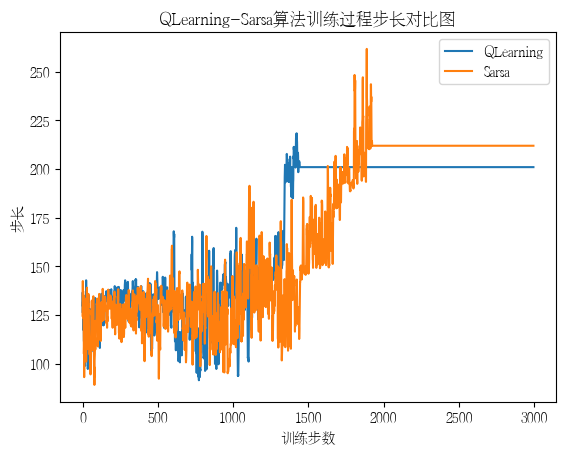
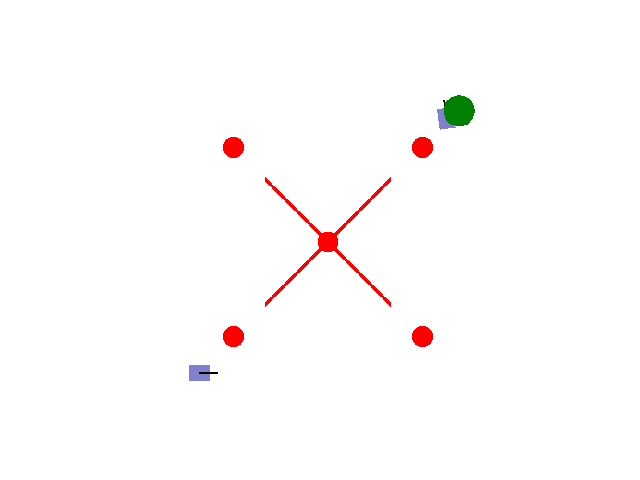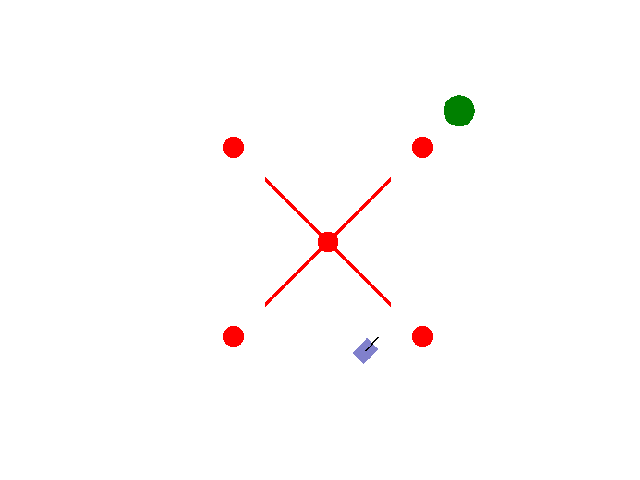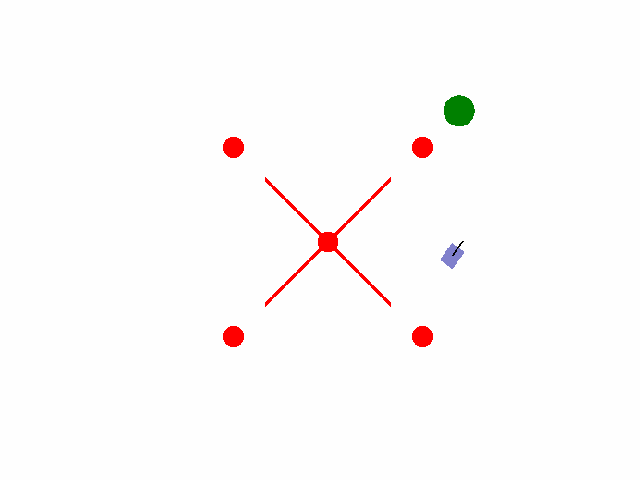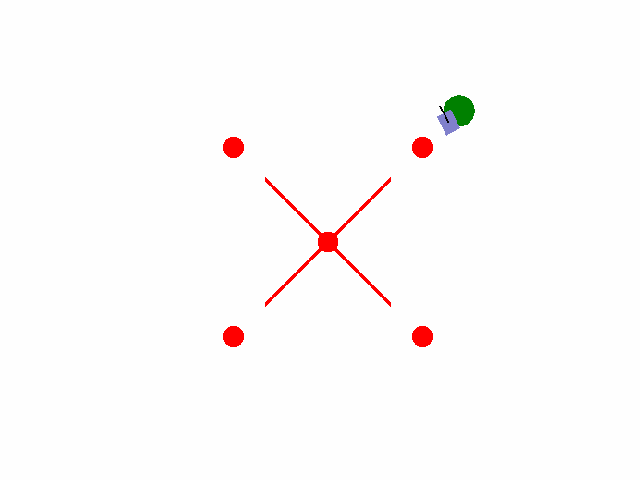



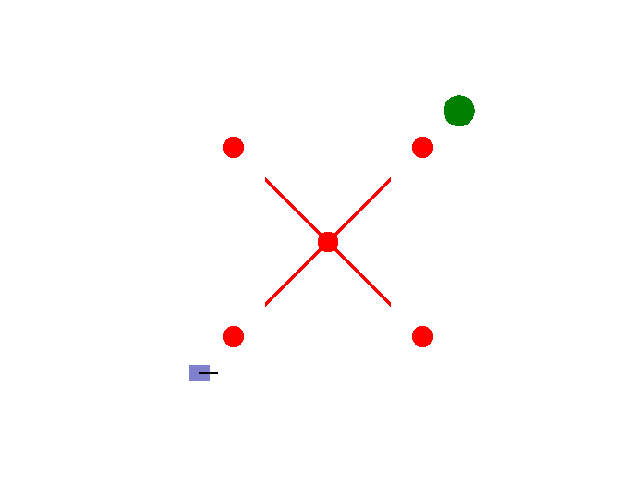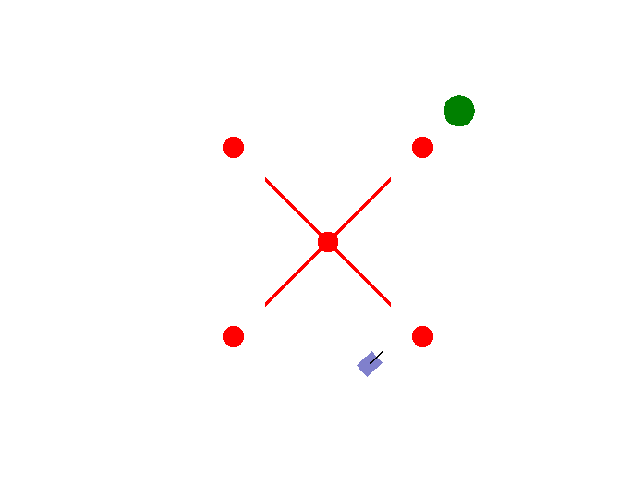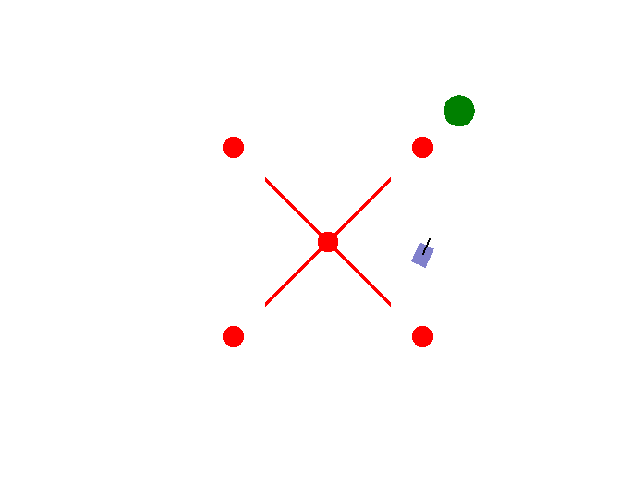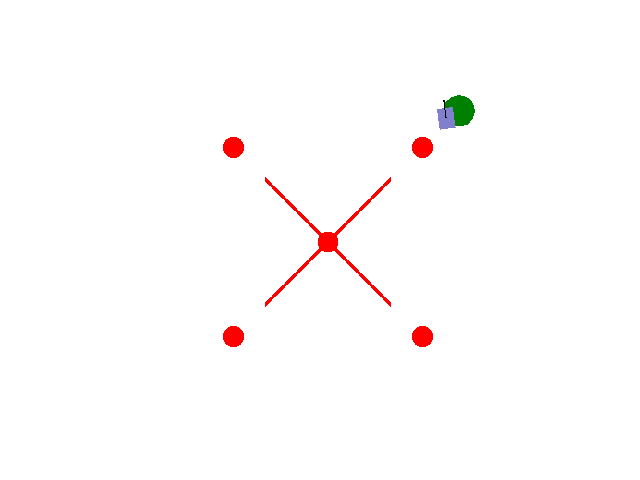
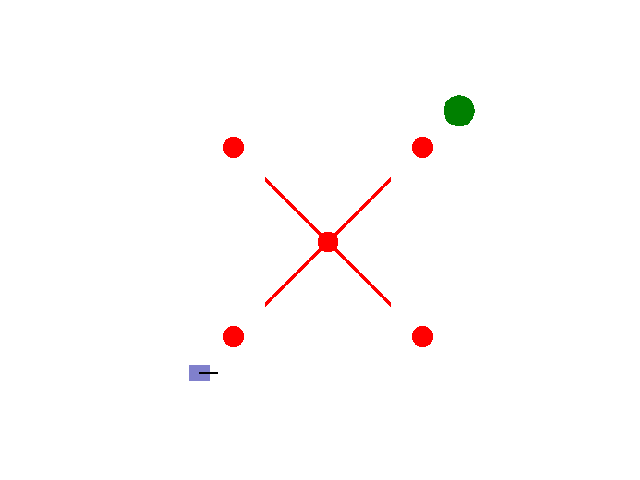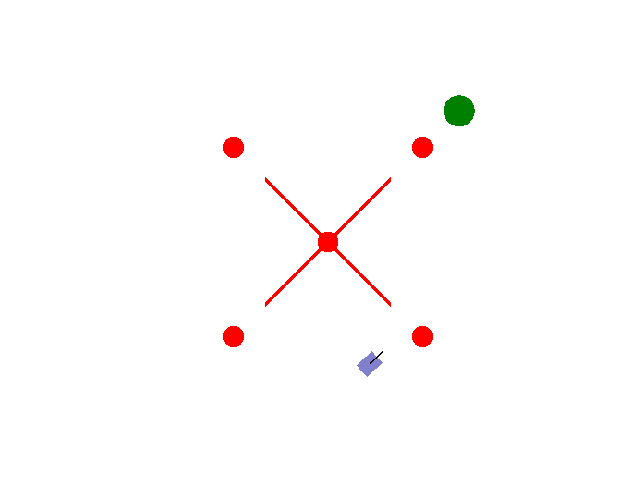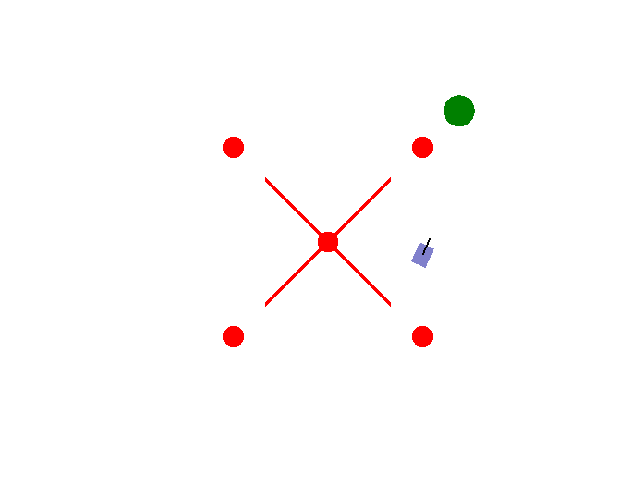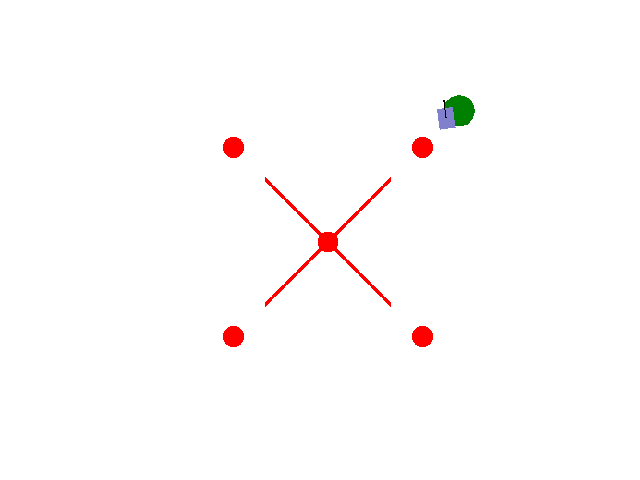
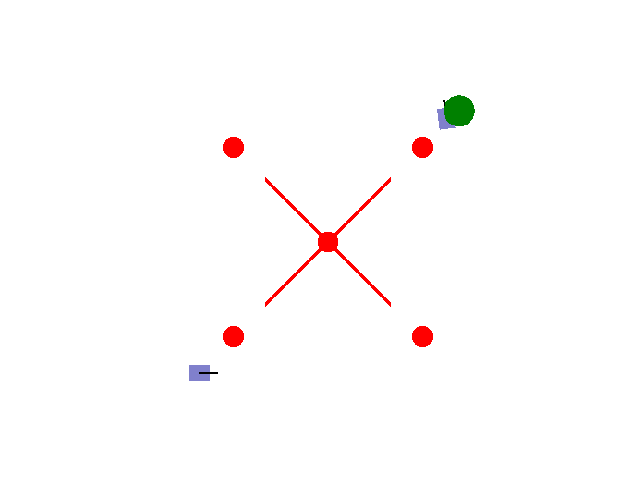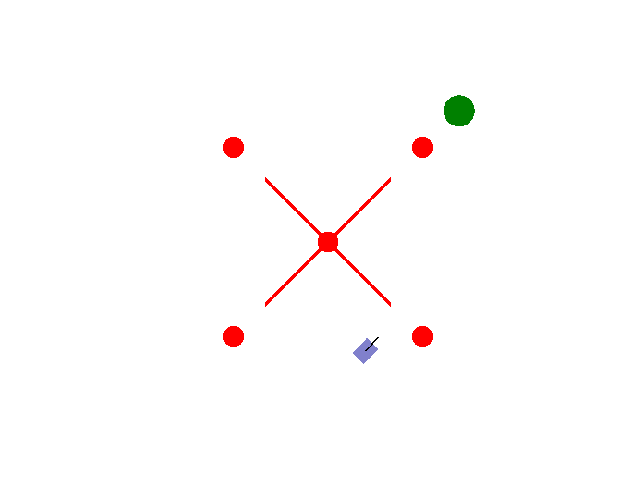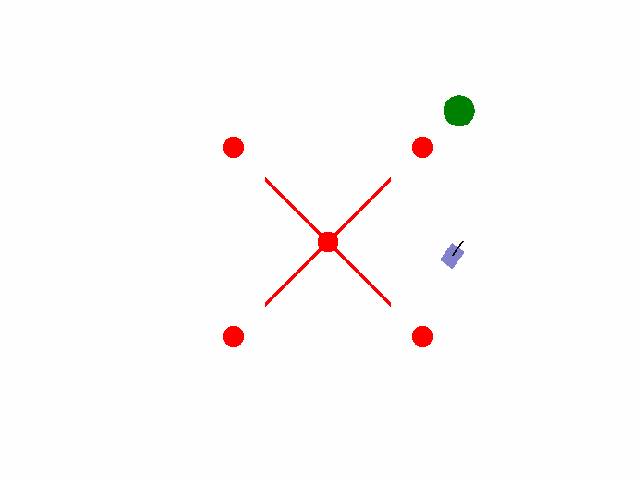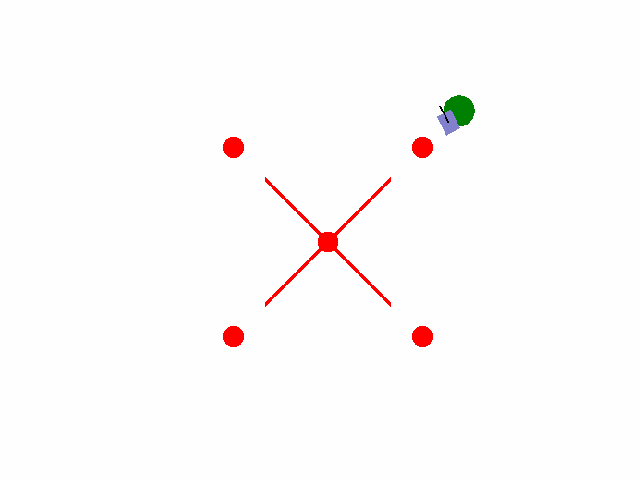



评论(6)
您还未登录,请登录后发表或查看评论